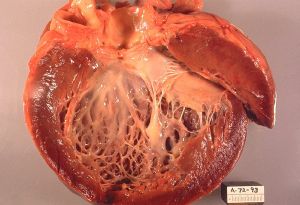
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Background
- Heart is dilated with poor contraction and EF
Causes
- Idiopathic (25% of CHF)
- Viral/chronic myocarditis (most common identifiable cause)
- Other causes
- Ischemic
- Other infectious - HIV, Lyme, Chagas
- Familial dilated cardiomyopathy
- Hypertensive dilated cardiomyopathy
- Toxic (ETOH/beriberi, cocaine, methamphetamine, chemo, heavy metals)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Sarcoidosis
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Kawasaki disease
- Autoimmune, SLE
- Connective tissue disease
- Infiltrative disease
- Mitochondrial disease
- Tachycardia-mediated
- ESRD
- Eosinophilic (Churg-Strauss syndrome)
Clinical Features
- CHF symptoms
Differential Diagnosis
Cardiomyopathy
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
Evaluation

ECGs of a patient with cardiomyopathy: LBBB accompanied by right access deviation (about 108°) and left atrial enlargement.
Workup
- CXR
- Cardiomegaly, pulmonary venous htn
- ECG
- LV hypertrophy, poor R wave progression
- Ultrasound
- Bedside (for gross function)
- TTE/TEE for EF
Diagnosis
- Typically on cardiac ultrasound (echo)
Management
- Treat the underlying disease
- Similar to CHF exacerbation
- Ensure exacerbation not due to ischemia
Disposition
- Admit for new diagnosis