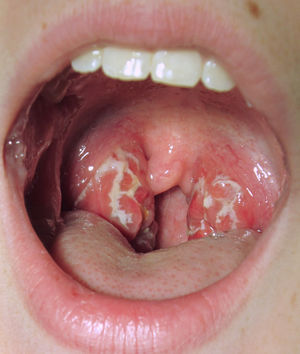
Streptococcal pharyngitis
Background[1]
- Peak in 5-15yr old
- Rare in <2yr of age
- Accounts for only 15-30% of pharyngitis
- Caused by S. pyogenes (Group A strep)
- Peak season is late winter / early spring
- Transmission is respiratory secretions
- Incubation period is 24-72 hours
- Antibiotics shorten symptoms by 16 hours
Clinical Features
- Sore throat
- Painful swallowing
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tonsillar exudate
- Palatal petechiae
Should NOT have a rash; if have scarlatiniform rash consider scarlet fever
Modified Centor Criteria[2]
One point is given for each of the criteria:[2]
- Absence of a cough
- Swollen and tender cervical lymph nodes
- Temperature >38.0 °C (100.4 °F)
- Tonsillar exudate or swelling
- Age less than 15^
- Subtract a point if age >44
| Points | Probability of Streptococcal pharyngitis |
|---|---|
| 1 or fewer | <10% |
| 2 | 11–17% |
| 3 | 28–35% |
| 4 or 5 | 52% |
Differential Diagnosis
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Scarlet fever
- Suppurative complications
Acute Sore Throat
Bacterial infections
- Streptococcal pharyngitis (Strep Throat)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Diphtheria (C. diptheriae)
- Bacterial Tracheitis
Viral infections
- Infectious mononucleosis (EBV)
- Patients with peritonsillar abscess have a 20% incidence of mononucleosis [3]
- Laryngitis
- Acute Bronchitis
- Rhinovirus
- Coronavirus
- Adenovirus
- Herpesvirus
- Influenza virus
- Coxsackie virus
- HIV (Acute Retroviral Syndrome)
Noninfectious
Other
- Deep neck space infection
- Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)
- Epiglottitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Penetrating injury
- Caustic ingestion
- Lemierre's syndrome
- Peritonsillar cellulitis
- Lymphoma
- Internal carotid artery aneurysm
- Oral Thrush
- Parotitis
- Post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage
- Vincent's angina
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Oral rashes and lesions
- Angioedema
- Aphthous stomatitis
- Herpes gingivostomatitis
- Herpes labialis
- Measles (Koplik's spots)
- Perioral dermatitis
- Oral thrush
- Steven Johnson syndrome
- Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Tongue diagnoses
- Vincent's angina
Evaluation
Diagnostic testing or empiric treatment of asymptomatic household contacts of patients with acute streptococcal pharyngitis is not routinely recommended
===Rapid Antigen Detection Test Algorithm (RADT)Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
- Dexamethasone 0.6mg/kg PO - maximum of 10mg
Disposition
- Discharge
Complications
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Scarlet fever
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Post-streptococcal glomerular nephritis
- PANDAS syndrome
- Peritonsillar abscess
- Cervical lymphadenitis
- Mastoiditis
See Also
References
- ↑ Choby BA. Amer Fam Phys. 2009, 79(5), 383-90.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Choby BA (March 2009). "Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis". Am Fam Physician 79 (5): 383–90. PMID 19275067.
- ↑ Melio, Frantz, and Laurel Berge. “Upper Respiratory Tract Infection.” In Rosen’s Emergency Medicine., 8th ed. Vol. 1, n.d.