Lumbar burst fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
{{Thoracic trauma DDX}} | |||
{{Lower back pain DDX}} | {{Lower back pain DDX}} | ||
== | ==Evaluation== | ||
*Obtain CT if unsure (vs. wedge) | *Obtain CT if unsure (vs. wedge) | ||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 24 October 2020
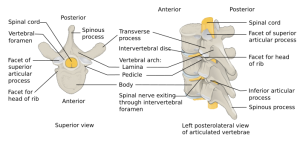
Background
- Unstable
- Can occur with or without injury to posterior elements (posterior involvement increases risk for neuro deficits)
- Can be confused with a wedge fracture (especially on plain films)
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Clinical Features
- Mechanism: axial load with failure of the anterior and middle columns
Differential Diagnosis
Thoracic Trauma
- Airway/Pulmonary
- Cardiac/Vascular
- Musculoskeletal
- Other
Lower Back Pain
- Spine related
- Acute ligamentous injury
- Acute muscle strain
- Disk herniation (Sciatica)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Spondylolithesis
- Epidural compression syndromes
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
- Cancer metastasis
- Spinal stenosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Discitis
- Spinal Infarct
- Renal disease
- Intra-abdominal
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Ulcer perforation
- Retrocecal appendicitis
- Large bowel obstruction
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic disease
- Other
Evaluation
- Obtain CT if unsure (vs. wedge)