Reactive arthritis: Difference between revisions
Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Ref should refer to facts in the article) |
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "Category:Rheum" to "Category:Rheumatology") |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Rheumatology]] | ||
Revision as of 16:17, 22 March 2016
Background
- Associated with bacterial infections
- Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, etc.
Clinical Features
- Can't see, Can't pee, Can't climb a tree
- (Classical triad in 1/3 of pts)
- Conjunctivitis or uveitis
- Nongonococcal urethritis
- Asymmetric oligoarthritis
- Keratoderma blennorrhagicum[1]
- Develops in 15% of pts
- Found on palm/soles. Vesicles/pustules with yellow/brown color. Appears similar to pustular psoriasis
Differential Diagnosis
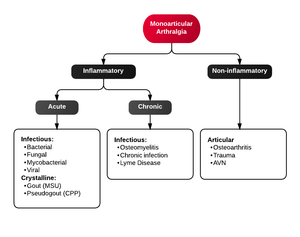
Monoarticular arthritis
- Acute osteoarthritis
- Avascular necrosis
- Crystal-induced (Gout, Pseudogout)
- Gonococcal arthritis, arthritis-dermatitis syndrome
- Nongonococcal septic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Malignancy (metastases, osteochondroma, osteoid osteoma)
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Trauma-induced arthritis
- Fracture
- Ligamentous injury
- Overuse
- Avascular necrosis
- Decompression sickness
- Spontaneous osteonecrosis
- Hemorrhagic (e.g. hemophilia, systemic anticoagulation
- Seronegative spondyloarthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis
- RA, SLE
- Sarcoidosis, amyloidosis
- Periarticular pathology
- Transient (Toxic) Synovitis (Hip)
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease
Oligoarthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Polyarthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reactive poststreptococcal arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Serum sickness
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Serum sickness–like reactions
- Viral arthritis
Migratory Arthritis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Lyme disease
- Rheumatic fever
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Viral arthritis
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis
- Must exclude gonococcal arthritis and other mimics
Management
- NSAIDs
- Antibiotics not needed for postdysentery form
- Consider doxycycline in chlamydia
Disposition
- Outpatient follow up, with DMARDs if refractory to NSAIDs
- 70% self-limited disease
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. The Skin in Immune, Autoimmune, and Rheumatic Disorders. In: Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. eds. Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology, 7e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.