Posterior vitreous detachment
Background
- A common age-related condition in which the vitreous gel that fills the eye separates from the retina.
- Separation of posterior vitreous from the retina, as a result of vitreous degeneration and shrinkage
- Usually benign, however in acute phase can occasionally lead to serious complications such as retinal tears or detachment [1].
- Prompt diagnosis and surgical treatment of retinal detachment can prevent impending vision loss or can restore vision
Risk factors
- Age (prevalence):
- 50-59 yrs = 24%
- 80-90 yrs = 87%
- Myopia
- Trauma
- Intraocular inflammation
- Ocular surgery[2]
Clinical Features
- Sudden onset of floaters (black spots, cobwebs)
- Flashes of light (photopsia), especially in peripheral vision
- A curtain or shadow in the visual field (if associated with retinal tear/detachment)
- Blurred vision or mild visual disturbances
- Often asymptomatic in early stages or in less dramatic detachments
Differential Diagnosis
Acute onset flashers and floaters
- Ocular causes
- Floaters and/or flashes
- Posterior vitreous detachment
- Retinal tear or retinal detachment
- Posterior uveitis
- Predominantly floaters
- Vitreous hemorrhage secondary to proliferative retinopathy
- Sympathetic ophthalmia
- Predominantly flashes
- Oculodigital stimulation
- Rapid eye movements
- Neovascular age-related macular degeneration
- Floaters and/or flashes
- Non-ocular causes
- Intraocular foreign body
- Migraine aura (classic)
- Migraine aura (acephalgicmigraine)
- Occipital lobe disorders
- Postural hypotension
Evaluation
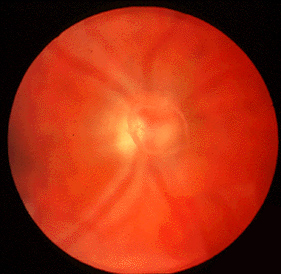
Fundoscopic exam showing a Weiss ring: a large, ring shaped floater that is sometimes seen if the vitreous body releases from the back of the eye.
Workup
- Detailed history (onset, nature of floaters/flashes, visual changes)
- Visual acuity testing
- Pupillary examination (look for afferent pupillary defect)
- Dilated fundoscopic exam (to assess for retinal tear or detachment)
- Slit-lamp exam with vitreous evaluation
- B-scan ocular ultrasound if fundus not visible due to hemorrhage or opacity [3]
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis based on symptoms and direct visualization of a detached posterior hyaloid membrane or Weiss ring on fundoscopic or slit-lamp exam
- Confirm absence of retinal tear or detachment via dilated eye exam or imaging
Management
- See disposition chart below
- No specific ED; focus of care is in determination of rapidity of ophthalmologic evaluation
Disposition
Referral of patients with presumed posterior vitreous detachment
| Clinical Assessment | Disposition |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Foos RY, Wheeler NC. Posterior vitreous detachment. Ophthalmology. 1982;89(12):1502–1512.
- ↑ Byer, N. E. (1994). Natural history of posterior vitreous detachment with early management as the premier line of defense against retinal detachment. Ophthalmology, 101(9), 1503–1513.
- ↑ American Academy of Ophthalmology. Posterior Vitreous Detachment. Accessed April 2025. https://www.aao.org



