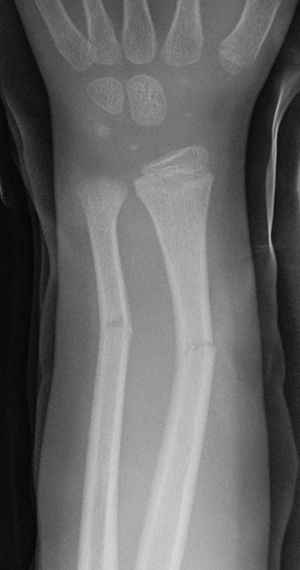
Greenstick fracture
Background
- Cortical disruption and periosteal tearing on convex side of bone only
- More stable / less painful than complete fracture
Clinical Features
- Pediatric fracture type
Differential Diagnosis
Evaluation
- Ultrasound scanning seems to be as sensitive as plain x-rays and may be better at demonstrating the degree of cortical deformity
Management
- Need for reduction determined by angulation, location, and age of child
- As a general rule, manipulation may be considered for deformity obvious to the naked eye or if more than the following acceptable angles[1]:
- >10 years old then < 10 degrees is acceptable.
- <10 years old then < 15 degrees is acceptable.
Traditionally these fractures have been treated by immobilisation in plaster for a period of around 3 to 6 weeks
- Fractures not requiring manipulation have a universally good outcome regardless of treatment
- Higher levels of patient satisfaction with a Futura type splint
Disposition
- Patients not requiring manipulation can be discharged with a backslab and advice to remove in 3 weeks or a Futura type splint and advice to remove when comfortable. There is no evidence that routine follow up is necessary.
See Also
References
- ↑ Cadman, E. Wrist torus and greenstick fractures, Don't Forget the Bubbles, 2019. Available at: http://doi.org/10.31440/DFTB.21125