Cervical facet dislocation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Hospital=== | ===Hospital=== | ||
===Bilateral=== | ====Bilateral==== | ||
*Unstable as whole column can sublux | *Unstable as whole column can sublux | ||
*high risk for significant spinal cord injury | *high risk for significant spinal cord injury | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
**operative management: nsg vs ortho | **operative management: nsg vs ortho | ||
===Unilateral=== | ====Unilateral==== | ||
*Relatively Stable | *Relatively Stable | ||
*Presentation | *Presentation | ||
Revision as of 04:01, 2 January 2015
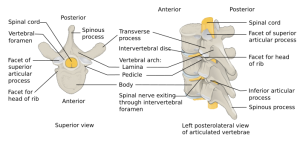
Background
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Workup
- C-Spine X-Ray
- determine if more than 1 spinal column affected
- 1 column = generally stable
- 2 or more columns = unstable
- generally superior facet fx
- abnormal xray? -> get CT
Management
Prehospital Immobilization
See NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization
Hospital
Bilateral
- Unstable as whole column can sublux
- high risk for significant spinal cord injury
- Disruption of annulus fibrosus and ant longitudinal ligament > ant displacement of spine
- Imaging
- Lateral xray: vertebral body will be displaced ~50% of its width
- Management
- spinal precautions
- operative management: nsg vs ortho
Unilateral
- Relatively Stable
- Presentation
- C5/C6: C6 radiculopathy with weakness to wrist extension numbness and tingling in the thumb
- C6/C7: C7 radiculopathy with weakness to triceps and wrist flexion and numbness in index and middle finger
- Imaging
- Lateral x-ray: vertebral body will be displaced ~25% of its width
- Anterior x-ray: affected spinous process points toward side that is dislocated
- Spinal cord injury rarely occurs