Cervical burst fracture: Difference between revisions
Ostermayer (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "Category:Ortho" to "Category:Orthopedics") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | *Prehospital Immobilization see [[EBQ:Prehospital Spine Immobilization|NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization]] | ||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
Revision as of 23:16, 10 May 2017
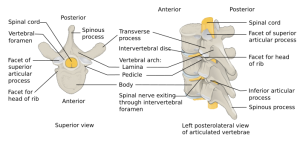
Background
- Unstable if:
- Associated neurologic deficits
- Loss of >50% of vertebral body height
- >20 degrees of spinal angulation
- Compromise of >50% of spinal canal
- Axial compression > nucleus pulposus forced into vertebral body
Clinical Features
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Workup
- Imaging
- Lateral x-ray - Comminuted body and loss of vertebral height
- AP x-ray - Vertical fracture of the body
Management
- Prehospital Immobilization see NAEMSP National Guidelines for Spinal Immobilization