Jefferson fracture: Difference between revisions
(added reference) |
(added ref section) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
*[[Unstable spine fractures]] | *[[Unstable spine fractures]] | ||
*[[Cervical spine injuries]] | *[[Cervical spine injuries]] | ||
==References== | |||
</references> | |||
[[Category:Trauma]] | [[Category:Trauma]] | ||
[[Category:Ortho]] | [[Category:Ortho]] | ||
Revision as of 08:50, 19 December 2015
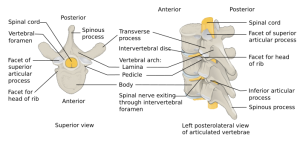
Background
- Also known as a C1 burst fracture
- No ligamentous disruption
- Is an unstable spine injury
Clinical Features
- Fx of the anteterior and posterior arches[1]
- Due to axial loading transmitted through occipital condyles to the lateral masses
Differential Diagnosis
Vertebral fractures and dislocations types
- Cervical fractures and dislocations
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
Diagnosis
- Suspect disruption if:
- Lateral x-ray: Increase in the predental space between C1 and dens (>3mm in adults, >5mm in children)
- Odontoid x-ray: Masses of C1 lie lateral to outer margins of articular pillars of C2
- If either of the above findings on x-ray obtain CT C-spine
Management
Prehospital Immobilization
Hospital
- Degree of instability determined by whether or not the transverse ligament is disrupted
- C-collar
- Consult ortho or spine as needed
Disposition
- Admit
See Also
References
</references>
- ↑ Jefferson, G. (1919) ‘Fracture of the atlas vertebra. Report of four cases, and a review of those previously recorded’, British Journal of Surgery, 7(27), pp. 407–422.