Stonefish envenomation: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[File:Stone Fish at AQWA SMC2006.jpg|thumb|Stonefish]] | [[File:Stone Fish at AQWA SMC2006.jpg|thumb|Stonefish]] | ||
*Synanceia is a genus of fish of the family Synanceiidae, the stonefish, whose members are venomous, dangerous, and even fatal to humans. They are the most venomous fish known.[1][2] They are found in the coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific. | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 11 March 2021
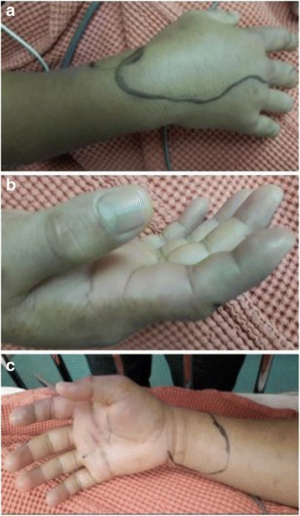
Background
- Synanceia is a genus of fish of the family Synanceiidae, the stonefish, whose members are venomous, dangerous, and even fatal to humans. They are the most venomous fish known.[1][2] They are found in the coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific.
Clinical Features
- Local erythema, ecchymosis, swelling
- Intense, sharp pain
- Systemic toxicity:
Differential Diagnosis
Marine toxins, envenomations, and bites
- Toxins
- Ciguatera
- Scombroid
- Tetrodotoxin (e.g. pufferfish)
- Shellfish poisoning
- Amnesic shellfish poisoning
- Diarrheal shellfish poisoning
- Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning
- Paralytic shellfish poisoning
- Stingers
- Venomous fish
- Cone shell
- Lionfish
- Sea urchins
- Crown-of-Thorns Starfish
- Stonefish
- Other: Catfish, zebrafish, scorpion fish
- Nematocysts
- Coral reef
- Fire coral
- Jellyfish (Cnidaria)
- Portuguese man-of-war
- Sea anemones
- Seabather's eruption
- Phylum porifera (sponges)
- Bites
- Infections
Evaluation
Workup
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis, no specific testing available
Management
- Clean wound, update tetanus, remove retained tissue
- One fifth of wounds develop local infection, but prophylactic antibiotics remain controversial [1]
- Immerse extremity in hot water (45 C) for 30-60 minutes
- Severe toxicity can be treated with antivenin obtained through poison control
Disposition
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ *Hobday D, Chadha P, Din AH, Geh J. Denaturing the Lionfish. Eplasty. 2016 May 23;16:ic20. PMID: 27298709; PMCID: PMC4892334.