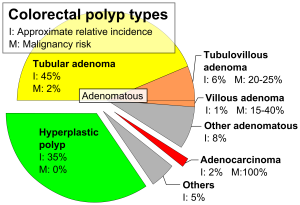
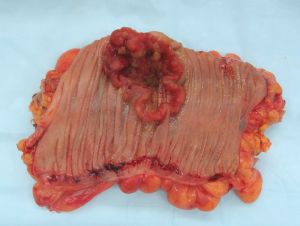
Colorectal cancer
(Redirected from Colon cancer)
Background

Average inner diameters and ranges of different sections of the large intestine.[1]
- Colorectal cancer is extremely common
Clinical Features
- Asymptomatic, frequently grow slowly for long period of time before symptomatic
- Lower GI bleeding (occult or visible BRBPR/hematochezia
- Fatigue, generalized weakness due to anemia
- Change in bowel habits, constipation, tenesmus in rectal cancer
- Obstruction if mass large enough (left colon > right)
- Abdominal pain
- Focal pain or Peritonitis if perforation
- Abdominal pain
- Signs/symptoms of metastatic disease (e.g. hepatomegaly, ascites, lymphadenopathy) may be initial presentation
Differential Diagnosis
Undifferentiated lower gastrointestinal bleeding
- Upper GI Bleeding
- Diverticular disease
- Vascular ectasia / angiodysplasia
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Infectious colitis
- Mesenteric Ischemia / ischemic colitis
- Meckel's diverticulum
- Colorectal cancer / polyps
- Hemorrhoids
- Aortoenteric fistula
- Nearly 100% mortality if untreated
- Consider in patients with gastrointestinal bleeding and known abdominal aortic aneurysms or aortic grafts
- Rectal foreign body
- Rectal ulcer (HIV, Syphilis, STI)
- Anal fissure
LLQ Pain
- Diverticulitis
- Kidney stone
- UTI
- Pyelonephritis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Infectious colitis
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis)
- Inguinal hernia
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Epiploic appendagitis
- Mittelschmerz
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian torsion
- PID
- Psoas abscess
- Testicular torsion
- Appendicitis
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Herpes zoster
- Endometriosis
- Colon cancer
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Small bowel obstruction
Anorectal Disorders
- Anal fissure
- Anal fistula
- Anal malignancy
- Anal tags
- Anorectal abscess
- Coccydynia
- Colorectal malignancy
- Condyloma acuminata
- Constipation
- Crohn's disease
- Cryptitis
- GC/Chlamydia
- Fecal impaction
- Hemorrhoids
- Levator ani syndrome
- Pedunculated polyp
- Pilonidal cyst
- Proctalgia fugax
- Proctitis
- Pruritus ani
- Enterobius (pinworms)
- Rectal foreign body
- Rectal prolapse
- Syphilitic fissure
Non-GI Look-a-Likes
Evaluation
- CBC, LFTs, coags if bleeding or signs of hepatic involvement
- CT abdomen- not definitive but may catch large mass or other alternative diagnoses
- Definitive diagnosis not likely to be made in ED, but suggestion of malignancy may be made on imaging if large mass seen
- Colonoscopy with biopsy
- Serum CEA
- Surgical pathology
Management
- Transfuse pRBCs prn for anemia
- Consult surgery for obstruction or perforation
- May also help coordinate outpatient diagnostic workup
Disposition
- Discharge if clinically stable
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Nguyen H, Loustaunau C, Facista A, Ramsey L, Hassounah N, Taylor H, et al. (July 2010). "Deficient Pms2, ERCC1, Ku86, CcOI in field defects during progression to colon cancer". Journal of Visualized Experiments (41). doi:10.3791/1931. PMC 3149991. PMID 20689513.