Pelvic ultrasound (transvaginal): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
***Thickened decidua on one side of uterine cavity surrounding anechoeic sac | ***Thickened decidua on one side of uterine cavity surrounding anechoeic sac | ||
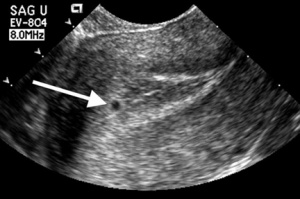
[[File:intradecidual sign.jpg|thumb|Intradecidual sign]] | [[File:intradecidual sign.jpg|thumb|Intradecidual sign]] | ||
*5.5-6 weeks: | *5.5-6 weeks: | ||
**Yolk Sac | **Yolk Sac | ||
***Circular (or sometimes as two parallel lines) echogenic structure with thick walls within gestational sac | ***Circular (or sometimes as two parallel lines) echogenic structure with thick walls within gestational sac | ||
*** | ***Definitive evidence of intrauterine pregnancy | ||
***Multiple yolk sacs is earliest sign in multiple gestational pregnancy | ***Multiple yolk sacs is earliest sign in multiple gestational pregnancy | ||
**Double bleb sign: | **Double bleb sign: | ||
| Line 114: | Line 108: | ||
**FHR ~170-180 bpm | **FHR ~170-180 bpm | ||
**Fetal movement visible | **Fetal movement visible | ||
**End of embryonic period | |||
==Images== | ==Images== | ||
| Line 123: | Line 118: | ||
===Abnormal=== | ===Abnormal=== | ||
Abnormal Pregnancy | |||
*Gestational sac >10mm without visible yolk sac | |||
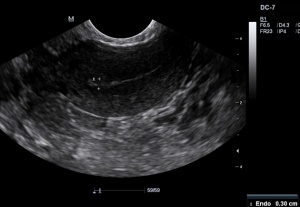
[[File:Iarge gestational sac|thumb|Gestational sac greater than 10mm without yolk sac, suggestive of abnormal pregnancy] | |||
*Gestational sac >18mm without fetal pole | |||
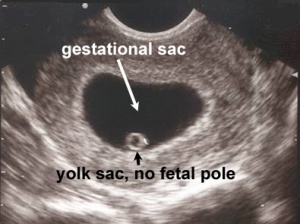
[[File:gestational sac without fetal pole.jpg|thumb|Gestational sac greater than 18mm without fetal pole, suggestive of abnormal pregnancy]] | |||
*Collapsed gestational sac | |||
*Pseudgestational sac | |||
**Endometrial breakdown during ectopic pregnancy | |||
**May be erroneously interpreted as true gestational sac in ectopic pregnancy | |||
**Irregularly shaped | |||
**Located in endometrial cavity, instead of eccentrically within endometrium | |||
**No yolk sac present | |||
**May not have double decidual sac sign | |||
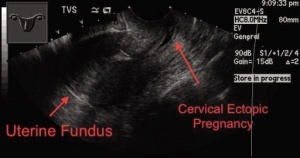
*Ectopic pregnancy | |||
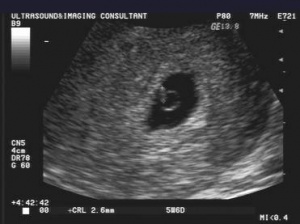
[[File:cervical ectopic.jpg|thumb|Ectopic pregnancy at the cervix]] | [[File:cervical ectopic.jpg|thumb|Ectopic pregnancy at the cervix]] | ||
Revision as of 21:29, 17 October 2017
Background
- Also known as endovaginal ultrasound
- Used to evaluate female reproductive organs including uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina
Indications
General
- Pelvic pain
- Abnormal pelvic or abdominal exam
Uterus
- Vaginal bleeding
- Fibroids
- IUD placement
Ovaries and adnexa
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian torsion
- Ovarian masses
- Tubo-ovarian abscesses
- Hydrosalpinx
Pregnancy
- Confirm intrauterine pregnancy
- Gestational dating
- Fetal monitoring and surveillance
- Evaluation of placenta
- Spontaneous abortion
- Intrauterine fetal demise
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Heterotopic pregnancy
- Molar pregnancy
Technique
- Use 5 MHz endocavitary probe (high frequency, low penetration)
- Apply surgical lubricant inside and outside probe cover
- Place patient in lithotomy position
- Gently advance probe into vaginal canal and position adjacent to cervix
- May be more comfortable for patient to insert probe into vagina herself
- Apply gentle pressure to lower abdominal wall with one hand and manipulate probe with other hand
Longitudinal scan
- Probe marker pointing at 12:00
- Shows anterior structures on left side of screen
- Begin midline at endometrial stripe
- Scan from right to left through uterus
- Move probe laterally to view adnexa and ovaries
Transverse scan
- Rotate probe 90 degrees so probe marker is pointing at 9:00
- Shows right-sided structures on left side of screen
- Start at endometrial stripe and scan throughout uterus
- Locate cornual flare (junction of uterus and fallopian tubes)
- Move probe laterally along fallopian tube to locate ovary
- Ovaries identified by follicular (anechoic or hypoechoic) structures
Findings
Uterus:
- Fundus pointing to anterior abdominal wall is anteverted
- Fundus pointing to posterior wall is retroverted
Endometrial stripe: Measured from thickest echogenic area (from one basal endometrial interface to the other, including canal)
- Pre-menopausal:
- During menstruation: 2-4mm
- Early proliferative phase: 5-7mm
- Late proliferative phase: 11mm
- Secretory phase: 7-16mm
- After D&C or SAB: >5mm
- Consider retained POC if thicker
- Post-menopausal:
- With vaginal bleeding: <5mm
- Without vaginal bleeding: <11mm
Adnexa:
- Simple ovarian cyst: <2.5-3cm
Pregnancy (1st trimester):
- 4-5 weeks:
- Gestational sac
- First sign of early pregnancy, usually seen between 3-5 weeks gestation
- Double decidual sac sign:
- Two concentric rings (uterine lining and gestation lining) around anechoic gestational sac
- Highly suggestive of intrauterine pregnancy (before yolk sac or embryo embryo visualized
- Gestational sac
- Intradecidual sign:
- Thickened decidua on one side of uterine cavity surrounding anechoeic sac
- Intradecidual sign:
- 5.5-6 weeks:
- Yolk Sac
- Circular (or sometimes as two parallel lines) echogenic structure with thick walls within gestational sac
- Definitive evidence of intrauterine pregnancy
- Multiple yolk sacs is earliest sign in multiple gestational pregnancy
- Double bleb sign:
- Yolk sac and amniotic cavity that look like two bubbles within gestational sac
- Yolk Sac
- 6-7 weeks
- Fetal Pole
- First visual manifestation of fetus (or "embryo")
- Thickening of margin on yolk sac
- Cardiac activity present (FHR ~100-115 bpm)
- Crown rump length: ~5mm
- Fetal Pole
- 8-9 weeks
- Limb buds appear
- Head identifiable
- 9-10 weeks
- FHR ~170-180 bpm
- Fetal movement visible
- End of embryonic period
Images
Normal
Abnormal
Abnormal Pregnancy
- Gestational sac >10mm without visible yolk sac
[[File:Iarge gestational sac|thumb|Gestational sac greater than 10mm without yolk sac, suggestive of abnormal pregnancy]
- Gestational sac >18mm without fetal pole
- Collapsed gestational sac
- Pseudgestational sac
- Endometrial breakdown during ectopic pregnancy
- May be erroneously interpreted as true gestational sac in ectopic pregnancy
- Irregularly shaped
- Located in endometrial cavity, instead of eccentrically within endometrium
- No yolk sac present
- May not have double decidual sac sign
- Ectopic pregnancy