Eczema herpeticum: Difference between revisions
(Text replacement - "OR" to "'''OR'''") |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*Development of vesicular eruptions in areas of epidermis previously affected by atopic dermatitis | *Development of vesicular eruptions containing HSV 1 or 2 in areas of epidermis previously affected by atopic dermatitis | ||
*Lesions may appear similar to impetigo (5) | |||
*fever is common | *fever is common | ||
*Multiple organ systems can be involved, resulting in lymphadenopathy, keratoconjunctivitis and resulting blindness, meningitis, encephalitis, etc (4). | |||
*Lesions may become secondarily infected by bacteria, mainly with staph aureus (4). | |||
*<3% of Eczema patients develop Eczema Herpeticum (4). | |||
*The following is associated with increased susceptibility to Eczema Herpeticum (2): | |||
**Early age of onset of eczema | |||
**History of food allergies or asthma (4) | |||
**Larger surface area of eczema | |||
**Eczema of the head/neck | |||
**Increased levels of IgE | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Eczema Herpeticum picture.png|Eczema Herpeticum in immunocompromised patient. Source: See references below ( | File:Eczema Herpeticum picture.png|Eczema Herpeticum in immunocompromised patient. Source: See references below (2). | ||
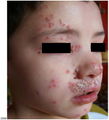
File: Eczema_Herpticum_picutre_2.jpg| Eczema herpticum in child. Source: see references below (4) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
{{HSV-1 DDX}} | {{HSV-1 DDX}} | ||
*Impetigo | |||
*Eczema Vaccinatum (5) | |||
*Primary varicella infection (5) | |||
== | ==Evaluation== | ||
*Clinical | |||
*Viral culture from swabs of wounds (5) | |||
*Tzanck smears showing multi-nucleated giant cells (5) | |||
*Direct Fluorescence antigen test for HSV (5) | |||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
*Treatment to cover [[Staph]] and [[Strep]] | *Treatment to cover [[Staph]] and [[Strep]] | ||
*[[Bactrim]] 10mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses OR [[clindamycin]] 24mg/kg/d divided into 3 doses x10d | *[[Bactrim]] 10mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses '''OR''' [[clindamycin]] 24mg/kg/d divided into 3 doses x10d | ||
*[[Acyclovir]] 80mg/kg/d in 3 divided doses x10 | *[[Acyclovir]] 80mg/kg/d in 3 divided doses x10 | ||
| Line 29: | Line 50: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
* Bagazgoitia L, Beà S, Garate M, Moreno R, Jaén P. ECZEMA HERPETICUM IN A PATIENT WITH TERMINAL RENAL FAILURE UNDER NARROW-BAND UVB THERAPY. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2010;55(2):200-201. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.62744. | *Aronson PL, Yan AC, Mittal MK, Mohamad Z, Shah SS. Delayed Acyclovir and Outcomes of Children Hospitalized With Eczema Herpeticum. Pediatrics. 2011;128(6):1161-1167. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0948. | ||
[[Category: | *Bagazgoitia L, Beà S, Garate M, Moreno R, Jaén P. ECZEMA HERPETICUM IN A PATIENT WITH TERMINAL RENAL FAILURE UNDER NARROW-BAND UVB THERAPY. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2010;55(2):200-201. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.62744. | ||
*Hinz T, Zaccaro D, Byron M, et al. ATOPIC DERMO-RESPIRAT'''OR'''Y SYNDROME IS A C'''OR'''RELATE OF ECZEMA HERPETICUM. Allergy. 2011;66(7):925-933. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02538.x. | |||
*Leung DYM. Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare? Antiviral research. 2013;98(2):153-157. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.02.010. | |||
*Liaw F-Y, Huang C-F, Hsueh J-T, Chiang C-P. Eczema herpeticum: A medical emergency. Canadian Family Physician. 2012;58(12):1358-1361. | |||
[[Category:Dermatology]] | |||
[[Category:ID]] | [[Category:ID]] | ||
Revision as of 00:47, 31 May 2017
Background
- May be life-threatening
Clinical Features
- Development of vesicular eruptions containing HSV 1 or 2 in areas of epidermis previously affected by atopic dermatitis
- Lesions may appear similar to impetigo (5)
- fever is common
- Multiple organ systems can be involved, resulting in lymphadenopathy, keratoconjunctivitis and resulting blindness, meningitis, encephalitis, etc (4).
- Lesions may become secondarily infected by bacteria, mainly with staph aureus (4).
- <3% of Eczema patients develop Eczema Herpeticum (4).
- The following is associated with increased susceptibility to Eczema Herpeticum (2):
- Early age of onset of eczema
- History of food allergies or asthma (4)
- Larger surface area of eczema
- Eczema of the head/neck
- Increased levels of IgE
Differential Diagnosis
Herpes Simplex Virus-1
- Eczema herpeticum
- Herpes gingivostomatitis
- Herpes keratitis
- Herpes labialis (cold sore)
- Herpes simplex encephalitis
- Herpetic whitlow
- Impetigo
- Eczema Vaccinatum (5)
- Primary varicella infection (5)
Evaluation
- Clinical
- Viral culture from swabs of wounds (5)
- Tzanck smears showing multi-nucleated giant cells (5)
- Direct Fluorescence antigen test for HSV (5)
Management
- Treatment to cover Staph and Strep
- Bactrim 10mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses OR clindamycin 24mg/kg/d divided into 3 doses x10d
- Acyclovir 80mg/kg/d in 3 divided doses x10
Disposition
See Also
External Links
References
- Aronson PL, Yan AC, Mittal MK, Mohamad Z, Shah SS. Delayed Acyclovir and Outcomes of Children Hospitalized With Eczema Herpeticum. Pediatrics. 2011;128(6):1161-1167. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-0948.
- Bagazgoitia L, Beà S, Garate M, Moreno R, Jaén P. ECZEMA HERPETICUM IN A PATIENT WITH TERMINAL RENAL FAILURE UNDER NARROW-BAND UVB THERAPY. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2010;55(2):200-201. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.62744.
- Hinz T, Zaccaro D, Byron M, et al. ATOPIC DERMO-RESPIRATORY SYNDROME IS A CORRELATE OF ECZEMA HERPETICUM. Allergy. 2011;66(7):925-933. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02538.x.
- Leung DYM. Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare? Antiviral research. 2013;98(2):153-157. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.02.010.
- Liaw F-Y, Huang C-F, Hsueh J-T, Chiang C-P. Eczema herpeticum: A medical emergency. Canadian Family Physician. 2012;58(12):1358-1361.