Ankylosing spondylitis
Revision as of 23:20, 17 October 2019 by ClaireLewis (talk | contribs)
Background
- Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the axial skeleton with variable involvement of other joints or even nonarticular structures
- 3x more common in males than females
- Typically diagnosed in young adults between the ages of 20 and 30 yrs
- Often associated with other autoimmune disorders
- 90% of people with AS express the HLA-B27 genotype
- Uveitis is common extra-articular manifestation, seen in 30% of patients
Clinical Features
- Spinal pain, particularly in the lower back, is usually the first and most common symptom of AS
- Begins in early adulthood (before 45 yrs)
- Has a gradual onset
- Lasts longer than three months
- Is worse after rest (for example, in the morning) but improves with activity
- Can cause morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
- Fatigue
- Can also be associated with anterior uveitis, arthritis, bowel ulcers and spine fractures (4 times more common in patients with AS [1])
Differential Diagnosis
Lower Back Pain
- Spine related
- Acute ligamentous injury
- Acute muscle strain
- Disk herniation (Sciatica)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Spondylolithesis
- Epidural compression syndromes
- Thoracic and lumbar fractures and dislocations
- Cancer metastasis
- Spinal stenosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Discitis
- Spinal Infarct
- Renal disease
- Intra-abdominal
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Ulcer perforation
- Retrocecal appendicitis
- Large bowel obstruction
- Pancreatitis
- Pelvic disease
- Other
Evaluation
- There is no direct test for AS
- ESR, CRP can be elevated but not sensitive or specific
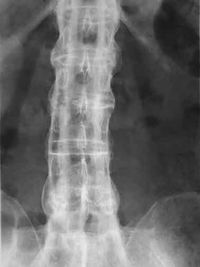
- Xray lumbar/sacroiliac: The earliest changes in the sacroiliac joints shows erosions and sclerosis
- Progression of erosions leads to pseudo widening of the joint space and bony ankylosis AKA "Bamboo Spine"
Often X-ray findings lag about 10 years from initial progression of disease
- CBC
- Chem 10
- Urinalysis
- Genetic testing for HLA B27 ( > 90% of people with AS have this gene, though by itself is not specific)
Management
- There is no cure for AS, although treatments (e.g. exercise, posture training) and medications can reduce symptoms and pain
- NSAIDS
- Sulfasalazine can be used in people with peripheral arthritis, but for axial involvement, evidence does not support it [2].
- Lack of evidence for methotrexate [3] or steroids.
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockers, such as the biologics etanercept, infliximab, golimumab and adalimumab, provide good short-term effectiveness though long term management is currently being studied
Disposition
- Often diagnosis will not be made in ED but if made in ED often can be discharged home with primary care follow up or rheumatology follow up
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Westerveld LA, Verlaan JJ, Oner FC. Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. European Spine Journal. 2009;18(2):145–156
- ↑ Chen J, Lin S, Liu C. Sulfasalazine for ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 11. Art. No.: CD004800. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004800.pub3.
- ↑ Chen J, Veras MMS, Liu C, Lin J. Methotrexate for ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD004524. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004524.pub4.