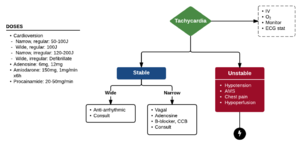
ACLS: Tachycardia
Revision as of 19:57, 18 July 2016 by Neil.m.young (talk | contribs) (Text replacement - "4 mg" to "4mg")
3 questions
- Is the patient in a sinus rhythm?
- Is the QRS wide or narrow?
- Is the rhythm regular or irregular?
Narrow
Narrow Regular
See also Tachycardia (Narrow)
- Sinus tachycardia
- Treat underlying cause
- SVT
- Vagal maneuvers (convert up to 25%)
- Adenosine 6mg IVP
- Can follow with 12mg if initially fails
- If adenosine fails, initiate rate control with CCB or BB
- Diltiazem 15-20mg IV, followed by infusion of 5-15mg/hr
- Metoprolol 5mg IVP x 3 followed by 50mg PO
- Synchronized Cardioversion (50-100J)
- Provide sedation prior to synchronized cardioversion if possible
Narrow Irregular
- MAT
- Treat underlying cause (hypoK, hypomag)
- Sinus Tachycardia with frequent PACs
- A fib / A Flutter with variable conduction (see also Atrial Fibrillation with RVR)
- Rate control with:
- Diltiazem
- MTP (good in setting of ACS)
- Amiodarone (good in setting of hypotension, CHF)
- Digoxin (good in setting of CHF)
- Synchronized Cardioversion (120-200 J)
- Rate control with:
Wide
Wide Regular
- If pulseless: shock (unsynchronized 200J)
- If unstable: shock (synchronized 100J)
- Hypotension, AMS, shock, ischemic chest discomfort, acute heart failure
- If stable:
- Meds
- Procainamide
- 20-50mg/min; then maintenance infusion of 1-4mg/min x6hr
- Treat until arrhythmia suppressed, QRS duration increases >50%, hypotension, Max 17mg/kg or 1 gram
- Avoid if prolonged QT or CHF
- Amiodarone
- 150mg over 10min (repeat as needed); then maintenance infusion of 1mg/min x6hr
- Adenosine
- May be considered for diagnosis and treatment only if rhythm is regular and monomorphic
- Procainamide
- Synchronized Cardioversion (100J)
- Meds
Wide Irregular
DO NOT use AV nodal blockers as they can precipitate V-Fib
- A fib with preexcitation
- 1st line - Electric Cardioversion
- 2nd line - Procainamide, amiodarone, or sotalol
- A fib with aberrancy
- Polymorphic V-Tach / Torsades De Pointes
- Give IV MgSO4
- Emergent defibrillation (NOT synchronized)
- Correct electrolyte abnormalities (esp hypoK, hypoMg)
- (Stop prolonged QT meds
See Also
External Links
References
2010 AHA ACLS Guidelines