Harbor: Base Hospital Resource for Physicians and MICNs
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center
- This is intended as a quick reference for Harbor-UCLA Base Hospital Physicians and MICNs.
Los Angeles County Prehospital Care Manual and Treatment Protocols
Types of Incoming Base Hospital Radio Calls
- 1. Base Contact (Medical direction by MICN, Attending, R4, R3)
- Includes traumatic injury, cardiac arrest, termination of resuscitation in the field, AMA
- 2. Base Notification (Medical direction by MICN, Attending, R4, R3)
- 3. Base to Base Referral (Medical direction by MICN or experienced Base Hospital Physician)
- 4. 911 Inter-facility Transport for Trauma (Attending Base Hospital Physician must take the report and accept patient)
- 5. 911 Inter-facility Transport for STEMI (Attending Base Hospital Physician must take the report and accept patient)
- 6. Multiple Casualty Incident (Medical direction by MICN or experienced Base Hospital Physician)
Common Provider Codes for Harbor-UCLA Base Hospital
- Most Commonly Used Provider Impression Codes
- ABOP = Abdominal Pain/Problems
- ETOH = Alcohol Intoxication
- ALOC = Altered Level of Conciousness-Not Hypoglycemia or Seizure
- PSYC = Behavioral/Psychiatric Crisis
- BRUE = BRUE
- CANT = Cardiac Arrest-Non-Traumatic
- CPNC = Chest Pain-Not Cardiac
- CPMI = Chest Pain-STEMI
- CPSC = Chest Pain-Suspected Cardiac
- DIZZ = Dizziness/Vertigo
- HYPR = Hyperglycemia
- HYTN = Hypertension
- HYPO = Hypoglycemia
- HOTN = Hypotension
- SOBB = Respiratory Distress/Bronchospasm
- RDOT = Respiratory Distress/Other
- CHFF = Respiratory Distress/Pulmonary Edema/CHF
- SEPI = Seizure-Postictal
- SEPS = Sepsis
- SHOK = Shock
- SYNC = Syncope/Near Syncope
- TRMA = Traumatic Injury
- WEAK = Weakness-General
- Common Paramedic Provider Agency Codes
- CF = Los Angeles County Fire
- CI = Los Angeles City Fire
- CM = Compton Fire
- MB = Manhattan Beach Fire
- RB = Redondo Beach Fire
- TF = Torrance Fire
- Most Common ECG Codes
- AFI = Atrial Fibrillation
- ASY = Asystole
- PEA = Pulseless Electrical Activity
- SR = Sinus Rhythm
- ST = Sinus Tachycardia
- VF = Ventricular Fibrillation
- VT = Ventricular Tachycardia
- Most Common Location Codes
- HO = Home
- NH = Nursing Home
- FR = Freeway
- ST = Street/Highway
- Most Common 9-1-1 Receiving Hospital Codes
- CNT = Centinela Hospital
- HGH = Harbor UCLA Medical Center
- KFH = Kaiser South Bay
- LCM = Providence Little Company of Mary Medical Center - Torrance
- MHG = Gardena Memorial Hospital
- MLK = Martin Luther King Hospital
- TOR = Torrance Memorial
Specialized Care and Transport Considerations
STEMI
- Medical management according to TP 1211
- Ensure Harbor-UCLA Medical Center is OPEN to STEMI by checking ReddiNet.
- ECG documentation (ECG section of the Base Contact Form)
- Initial Rhythm, 12-Lead ECG @ (time), EMS Interpretation, Software Interpretation.
- Obtain transmitted ECG from Harbor-UCLA STEMI outlook email.
- Discuss with Attending regarding STEMI page out and cath lab activation prior to patient arrival.
- Destination: STEMI Receiving Center (SRC)
Stroke
- Medical management according to TP 1232
- On all patients exhibiting local neurologic signs, paramedics must perform and report:
- 1. Modified Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (mLAPSS)
- 2. If mLAPSS positive --> Document Los Angeles Motor Scale (LAMS) score (1 to 5) and Last Known Well Time (LKWT)
- MUST document mLAPSS +/- LAMS/LKWT on the Base Contact Form (Assessment Section) for provider impression Stroke/CVA/TIA (STRK)
- Prehospital stroke evaluation tools
- mLAPSS[1]: A decision tool designed to rapidly differentiate acute strokes that may benefit from expedited acute stroke therapy from stroke mimics in the field.
- LAMS Score[2]: A validated score to predict large vessel occlusion in the field.
- LAMS ≥4 showed sn 81%, sp 89%, and overall accuracy 85% for predicting LVO.[3]
- Destination:
- If mLAPSS positive, LAMS 4-5, LKWT < 24 hours -> Transport to Comprehensive Stroke Center (CSC) if within 30 min
- If mLAPSS positive, LAMS ≤ 3, LKWT < 24 hours -> Transport to closest Stroke Center (Primary or Comprehensive)
- mLAPSS negative but acute stroke suspected -> Transport destination is at the discretion of Base Hospital
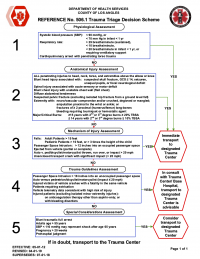
Trauma
- Medical management according to TP 1244 for adults, TP 1244-P for pediatrics.
- Any patient that meets trauma criteria or is deemed by provider judgment to meet trauma criteria should be transported to the nearest adult or pediatric trauma center.
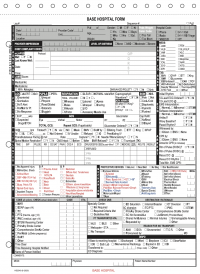
- Trauma criteria can be found on the Base Contact Form under the TRAUMA and MECHANISM Sections. Patients are classified as a trauma patient if any of the red boxes are checked.
- Pediatric Trauma Center Criteria
- Children >15 years old cannot go to an adult trauma center
- Destination: Adult or Pediatric Trauma Center
Burns
- Medical management according to TP 1220 for adults and TP 1220-P for pediatrics.
- If a burn patient meets Trauma Center criteria, then transport to Trauma Center.
- If NO SIGNS OF TRAUMA, consider transport to directly to a burn center if they meet these criteria:
- ≥ 15 years with 2nd and 3rd degree burn ≥ 20% TBSA
- ≤ 14 years with 2nd and 3rd degree burn ≥ 10% TBSA
- If the patient does not meet burn center criteria and has NO SIGNS OF TRAUMA, transport to Most Accessible Receiving Center (MAR)
- Destination: Burn center, Trauma center, or MAR
Types of Destinations/Receiving Centers
- MAR = Most Accessible Receiving
- TC = Trauma Center
- EDAP = Emergency Department Approved for Pediatrics
- Think of an EDAP as a MAR for children approved to care for children ≤ 14 years old.
- PMC = Pediatric Medical Center
- Approved to care for critically ill children ≤ 14 years old.
- PTC = Pediatric Trauma Center
- Approved to care for children ≤ 14 years old who meet trauma criteria.
- Perinatal Center
- Basic ED with 24/7 Obestrical services approved to care for pregnant patients >20 weeks gestation.
- SRC = STEMI Receiving Center
- PSC = Primary Stroke Center
- Able to care for most ischemic strokes.
- CSC = Comprehensive Stroke Center
- Able to care for all ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke cases with 24/7 neurosurgery and capable of performing minimally invasive catheter-based procedures including thrombectomy for large vessel occlusion strokes.
Management of Non-Traumatic Cardiac Arrest and Termination of Resuscitation
- Cardiac arrest should be managed based on TP 1210
- Goal of OHCA resuscitation: Survival with good neurological outcome.
- All patients in cardiac arrest should also be transported to an SRC if transport time is <30 minutes.
- Termination of Resuscitation based on presenting rhythm:
- Non-shockable Rhythms (Aystole or PEA)
- If the patient remains in asystole for 20 minutes of EMS personnel CPR, AND meets all of the following criteria, EMS personnel may determine death without base contact per Ref No. 814.
- 1. Patient 18 years or greater
- 2. Arrest not witnessed by EMS personnel
- 3. No shockable rhythm identified at any time during the resuscitation
- 4. No ROSC at any time during the resuscitation
- 5. No hypothermia
- If all these criteria are not met (including any PEA rhythm), base physician consultation is required for the determination of death and termination of resuscitation in the field.
- If the patient remains in asystole for 20 minutes of EMS personnel CPR, AND meets all of the following criteria, EMS personnel may determine death without base contact per Ref No. 814.
- Shockable Rhythms (Vfib or Vtach)
- Resuscitation should be continued for approximately 40 minutes on scene. Base physician consultation is required for the determination of death and termination of resuscitation in the field.
- Non-shockable Rhythms (Aystole or PEA)
- Transportation without ROSC is discouraged.
- Special circumstances for transportation without ROSC include scene safety concerns, family disagreement with the decision to terminate resuscitation, resuscitation taking place in the back of the ambulance.
Base Contact For A Patient Refusing Transport
- Ref No. 834
- In Los Angeles County, paramedics should not refuse transport and should honor any request by a patient for transport.
- AMA
- Adults
- Paramedics are required to make base contact for any patient leaving AMA.
- An adult with an ongoing medical emergency may refuse transport if they have decision making capacity. The patient must understand and state the risks of leaving AMA. It is highly recommended that the base hospital provider speak with the patient prior to leaving AMA.
- For patients without decision-making capacity who are refusing transport, assistance from law enforcement should be requested.
- Pediatrics
- Pediatric patients with an ongoing medical emergency should be transported under implied consent. If the parent refuses transport for a child with an ongoing medical emergency that requires transport, assistance from law enforcement should be requested.
- Adults
- Treat and Refer
- For patients without an ongoing medical emergency and with decision-making capacity (or guardian present), the patient may be released at the scene. Base contact is not required.
911 Interfacility Transport (IFT) Trauma Re-Triage
- A system developed to handle walk-in trauma patients or undertriage of trauma patients by EMS to non-trauma centers.
- The patient MUST meet one of the 8 defined criteria or else may be a candidate for MAC transfer.
- Criteria #8: Patients, who in the judgment of the evaluating emergency physician, have a high likelihood of requiring emergent life- or limb-saving intervention within two hours.
- Consider that some interventions performed at the sending facility may be out of the scope of paramedics (e.g. paralyzing agents, blood products, vasopressors, sedation medications). In select cases, the sending facility may have to send a physician or nurse with the transport crew.
Medications in Paramedic Scope of Practice
- It is important to remember that not all provider agencies may stock all medications within the paramedic scope and that each medication is only approved in the prehospital setting for specific indications.
- Approved ALS medications in Los Angeles County
- Adenosine
- Albuterol
- Amiodarone
- Aspirin
- Atropine
- Calcium Chloride
- Dextrose
- Diphenhydramine
- Epinephrine
- Fentanyl
- Glucagon
- Ketorolac
- Lidocaine
- Midazolam
- Morphine Sulfate
- Naloxone
- Nitroglycerin
- Ondansetron
- Oxygen
- Pralidoxime Chloride (DuoDote™)
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Ref No. 1300
ReddiNet
- A designated emergency and disaster communication system established for hospitals within Los Angeles County.
- Allows Los Angeles County hospitals to request diversion status, manage MCIs, and report bed availability.
- It is the responsibility of each hospital to ensure ReddiNet remains up to date and online at all times.
- Diversion requests Categories
- Hospitals may request ED Sat in 1 hour increments if unable to care for ALS patients. BLS traffic is not diverted.
- Other diversion categories include: CT Scanner, Trauma, Peds, STEMI, Stroke, Internal disaster (only category in which both ALS and BLS are diverted)
- See Ref No. 503
Fundamental Concepts of Base Hospital Contact
- Ref No. 1200.2
- Base contact is required for specific provider impressions or if certain treatments or medications are administered.
- Paramedics are licensed providers and able to practice independently based on established treatment protocols (Off-line Medical Direction).
- During base contact, physicians and MICNs may direct paramedics to deliver treatments outside established protocols as long as it is within their scope of practice or bypass MAR if there is a clear indication to do so (On-line Medical Direction).
- When providing on-line medical direction, be clear and direct, offer a brief explanation with the order, document appropriately on the base hospital form.
Base Contact Form Documentation Reminders
- GEN INFO Section
- Document Time in Military Time
- Document Weight in Kgs
- It is ok to approximate weight by dividing lbs by 2 (ex. If medics state the patient is 100lbs, you can respond: "To confirm the patient is 100lbs or approximately 50kgs").
- ASSESSMENT Section
- Ask providers to obtain family contact information and/or bring along DNR/AHCD/POLST if relevant.
- PHYSICAL Section
- Document capnography # for all patients receiving positive pressure.
- VITALS & TXS Section
- Document a pain level when ordering PRN analgesia (ex. Morphine 4mg IV PRN pain >5/10).
- ECG Section
- Document the time that ECG was taken.
- ARREST Section
- Ensure Time of Resus D/C is documented when relevant.
See Also
External Links
References
- ↑ Kidwell CS, Starkman S, Eckstein M, et al. Identifying stroke in the field. Prospective validation of the Los Angeles prehospital stroke screen (LAPSS). Stroke. 2000 Jan;31(1):71-6. doi: 10.1161/01.str.31.1.71. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/01.STR.31.1.71
- ↑ Llanes JN, Kidwell CS, Starkman S, Leary MC, Eckstein M, Saver JL. The Los Angeles Motor Scale (LAMS): a new measure to characterize stroke severity in the field. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2004 Jan-Mar;8(1):46-50. doi: 10.1080/312703002806. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/312703002806
- ↑ Nazliel B, Starkman S, Liebeskind DS, et al. A brief prehospital stroke severity scale identifies ischemic stroke patients harboring persisting large arterial occlusions. Stroke. 2008;39(8):2264-2267. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.508127 https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.508127