Tricyclic antidepressant toxicity
Background
- Serious toxicity is almost always seen within 6hr of ingestion
- Ingestion amount:
- <1mg/kg: Nontoxic
- >10mg/kg: Life-threatening
- >1gm: Commonly fatal
- Coingestants often increase severity of toxicity
Clinical Features
- Na Channel Blockade
- Negative inotropy, heart block, hypotension, ectopy
- Anti-Histamine Effects
- Sedation, coma
- Anti-Muscarinic Effects
- Central
- Agitation, delirium, confusion, hallucinations
- Slurred speech, ataxia
- Sedation, coma
- Seizures
- Peripheral
- Mydriasis, decreased secretions, dry skin, ileus, urinary retention
- Tachycardia, hyperthermia
- Central
- Alpha1 Receptor Blockade
- Sedation, orthostatic hypotension, miosis
- Inhibition of amine reuptake
- Sympathomimetic effects
- Myoclonus, hyperreflexia
- Serotonin Syndrome (only when used in combination w/ other serotonergic agents)
Diagnosis
- Serious toxicity
- Conduction delays, SVT, V-tach, hypotension
- Respiratory depression
- Seizures
- Pulmonary Edema
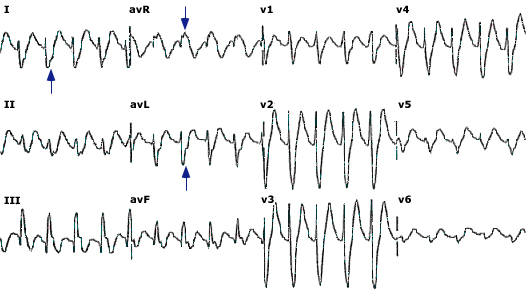
- ECG
- Sinus Tachycardia (most frequent dysrhythmia)
- PR, QRS, QT Prolongation
- Right axis deviation (of terminal 40ms)
- Terminal R wave in aVR, S wave in I/aVL[1]
- Brugada pattern (15%)[2]
Treatment
GI Decontamination
- Gastric lavage if <1hr after ingestion
- Activated charcoal 1gm/kg x1
Cardiac Toxicity[3]
Sodium Bicarbonate
- Indications:
- QRS >100ms, terminal RAD >120 deg, Brugada pattern, ventricular dysrhythmias
- Initial Dosing:
- Give 1-2 mEq/kg as rapid IVP; may repeat as necessary (stop if pH > 7.55)
- May give as 2-3 vials or prefilled syringes (50mL each) of 8.4% NaHCO3
- Infusion Dosing
- Mix 125-150 mEq of NaHCO3 in 1L of D5W; infuse at 250 mL/hr
- Treatment Goal:
- QRS <100ms
- pH 7.50-7.55
- Treatment Monitoring
- Monitor for volume overload, hypokalemia, hypernatremia, metabolic alkalosis
Hyperventilation
- Consider in patients unable to tolerate NaHCO3 (renal failure, pulm/cerebral edema)
Lidocaine
- Consider for ventricular dysrhythmias if NaHCO3 alone is ineffective
- NOTE
- avoid IA, IB, IC antiarrhythmics, Beta-Blockers, and Calcium Channel Blockers
Phenytoin
- Consider for ventricular dysrhythmias resistant to NaHCO3 and lidocaine
Synchronized cardioversion
- Appropriate in pts w/ persistent unstable tachydysrhythmias
Seizures
- Benzodiazapines are 1st line
- Barbituates or Propofol are 2nd line
Hypotension
- After repeat fluid boluses and with sodium load from NaHCO3 norepinepherine should be the first line vasopressor
- ECMO is a successful adjunct for refractory hypotension after maximal therapy has failed
Dialysis
Not useful for enhancing elimination due to the large volume of distribution and high lipid solubility
Disposition
- Consider discharge for pts who remain asymptomatic after 6hr of observation
See Also
Source
- Tintinalli
- UpToDate
- ↑ Liebelt EL, Francis PD, Woolf AD. ECG lead aVR versus QRS interval in predicting seizures and arrhythmias in acute tricyclic antidepressant toxicity. Ann Emerg Med. Aug 1995;26(2):195-201
- ↑ Monteban-Kooistra WE, van den Berg MP, Tulleken JE. Brugada electrocardiographic pattern elicited by cyclic antidepressants overdose. Intensive Care Med. Feb 2006;32(2):281-5
- ↑ Thanacoody HK, Thomas SH. Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning: cardiovascular toxicity. Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(3):205-14