Tricyclic antidepressant toxicity
Background
- Serious toxicity is almost always seen within 6hr of ingestion
- Ingestion amount:
- <1mg/kg: Nontoxic
- >10mg/kg: Life-threatening
- >1gm: Commonly fatal
- Coingestants often increase severity of toxicity
Clinical Features
- Na Channel Blockade
- Negative inotropy, heart block, hypotension, ectopy
- Anti-Histamine Effects
- Sedation, coma
- Anti-Muscarinic Effects
- Central
- Agitation, delirium, confusion, hallucinations
- Slurred speech, ataxia
- Sedation, coma
- Seizures
- Peripheral
- Mydriasis, decreased secretions, dry skin, ileus, urinary retention
- Tachycardia, hyperthermia
- Central
- Alpha1 Receptor Blockade
- Sedation, orthostatic hypotension, miosis
- Inhibition of amine reuptake
- Sympathomimetic effects
- Myoclonus, hyperreflexia
- Serotonin Syndrome (only when used in combination w/ other serotonergic agents)
Diagnosis
- Serious toxicity
- Conduction delays, SVT, V-tach, hypotension
- Respiratory depression
- Seizures
- Pulmonary edema
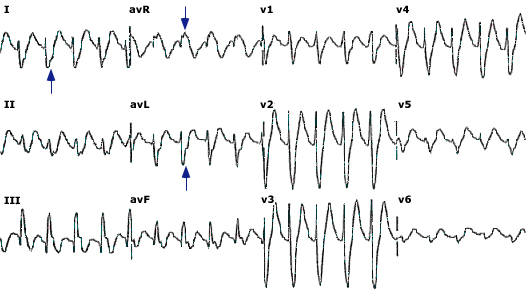
- ECG
- Sinus tachycardia (most frequent dysrhythmia)
- PR, QRS, QT prolongation
- Right axis deviation (of terminal 40ms)
- Terminal R wave in aVR, S wave in I/aVL
- Brugada pattern (15%)
Treatment
- GI Decontamination
- Gastric lavage if <1hr after ingestion
- Activated charcoal 1gm/kg x1
- Cardiac Toxicity
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Indications:
- QRS >100ms, terminal RAD >120deg, Brugada pattern, ventricular dysrhythmias
- Dosing
- Give 1-2 mEq/kg as rapid IVP; may repeat as necessary (stop if pH > 7.55)
- May give as 2-3 vials or prefilled syringes (50mL each) of 8.4% NaHCO3
- If effective, start infusion
- Mix 125-150 mEq of NaHCO3 in 1L of D5W; infuse at 250 mL/hr
- Give 1-2 mEq/kg as rapid IVP; may repeat as necessary (stop if pH > 7.55)
- Goal
- QRS <100ms
- pH 7.50-7.55
- Monitoring
- Monitor for volume overload, hypokalemia, hypernatremia, metabolic alkalosis
- Indications:
- Hyperventilation
- Consider in pts unable to tolerate NaHCO3 (renal failure, pulm/cerebral edema)
- Lidocaine
- Consider for ventricular dysrhythmias if NaHCO3 alone is ineffective
- Phenytoin
- Consider for ventricular dysrhythmias resistant to NaHCO3 and lidocaine
- Synchronized cardioversion
- Appropriate in pts w/ persistent unstable tachydysrhythmias
- Avoid IA, IB, IC, BBs, and CCBs
- Sodium Bicarbonate
- Seizures
- Benzodiazapines are 1st line
- Barbitutate are 2nd line
- Phenytoin is ineffective
- Hypotension
- IVF 10mL/kg; pulmonary edema can develop if excessive fluids given
- Give NaHCO3 if fluids ineffective (regardless of QRS duration)
- Give norepi if fluids/NaHCO3 ineffective
- Start 1mcg/min; tirate up to 30mcg/min
- Dialysis not useful
Disposition
- Consider discharge for pts who remain asymptomatic after 6hr of observation
See Also
Source
- Tintinalli
- UpToDate