Lower back pain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Pain lasting >6wks is risk factor for more serious disease | *Pain lasting >6wks is risk factor for more serious disease | ||
*Back pain in IV drug user is spinal infection until proven otherwise | |||
*Night pain and unrelenting pain are worrisome symptoms | |||
==Clinical Features== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*See [[Back Pain (Red Flags)]] | |||
*Musculoskeletal pain | *Musculoskeletal pain | ||
**Located primarily in the back w/ possible radiation into the buttock/thighs | **Located primarily in the back w/ possible radiation into the buttock/thighs | ||
**Pain worse w/ movement but improves w/ rest | |||
*Spinal stenosis | |||
**Bilateral sciatic pain worsened by walking, prolonged standing; relieved by forward flexion | |||
*Sciatica | *Sciatica | ||
**Refers to radicular back pain in the distribution of a lumbar or sacral nerve root | **Refers to radicular back pain in the distribution of a lumbar or sacral nerve root | ||
** | **Pain worsened by coughing, Valsalva, sitting; relieved by lying in supine position | ||
**Occurs in only 1% of pts w/ back pain | **Occurs in only 1% of pts w/ back pain | ||
**95% of herniated disks occur at the L4-L5 or L5-S1 disk spaces | **95% of herniated disks occur at the L4-L5 or L5-S1 disk spaces | ||
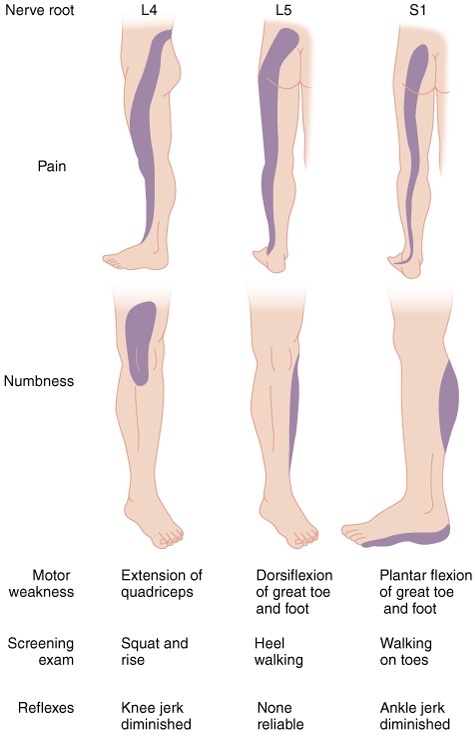
[[File:Lumbar_Nerve_Root_Compromise.jpg]] | |||
==DDX== | |||
*See [[Back Pain (DDX)]] | |||
== Work-Up == | == Work-Up == | ||
#Pregnancy test | #Pregnancy test | ||
#Straight leg raise testing | #Exam | ||
## | ##Straight leg raise testing | ||
#X-rays | ###Screening exam for a herniated disk (Sn 68-80%) | ||
###Lifting leg causes radicular pain of affected leg radiating to BELOW the knee | |||
###Pain is worsened by ankle dorsiflexion | |||
##Crossed Straight leg raise testing (high Sp, low Sn) | |||
###Lifting the asymptomatic leg causes radicular pain down the affected leg | |||
##Nerve root compromise | |||
#X-rays (if have red flag) | |||
##Adults: AP + lateral of lumbar spine | ##Adults: AP + lateral of lumbar spine | ||
##Children: add oblique views (to evaluate for spondylolisthesis) | ##Children: add oblique views (to evaluate for spondylolisthesis) | ||
#Labs | #Labs | ||
##CBC/ESR/Chem 7/UA (if >50 yo) | ##CBC/ESR/Chem 7/UA (if >50 yo) | ||
#MRI | |||
##Indications: | |||
####Suspect disk disease w/ severe motor impairment | |||
####Suspect abscess or metastases w/ neuro involvement | |||
#Cauda equina syndrome | |||
#?Elevated ESR | |||
#US | #US | ||
##Rule-out AAA | ##Rule-out AAA | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
*[[Back Pain (Red Flags)]] | *[[Back Pain (Red Flags)]] | ||
*See [[Back Pain (DDX)]] | |||
== Source == | == Source == | ||
*Tintinalli | |||
[[Category:Ortho]] | [[Category:Ortho]] | ||
Revision as of 05:25, 19 February 2012
Background
- Pain lasting >6wks is risk factor for more serious disease
- Back pain in IV drug user is spinal infection until proven otherwise
- Night pain and unrelenting pain are worrisome symptoms
Clinical Features
- See Back Pain (Red Flags)
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Located primarily in the back w/ possible radiation into the buttock/thighs
- Pain worse w/ movement but improves w/ rest
- Spinal stenosis
- Bilateral sciatic pain worsened by walking, prolonged standing; relieved by forward flexion
- Sciatica
- Refers to radicular back pain in the distribution of a lumbar or sacral nerve root
- Pain worsened by coughing, Valsalva, sitting; relieved by lying in supine position
- Occurs in only 1% of pts w/ back pain
- 95% of herniated disks occur at the L4-L5 or L5-S1 disk spaces
DDX
- See Back Pain (DDX)
Work-Up
- Pregnancy test
- Exam
- Straight leg raise testing
- Screening exam for a herniated disk (Sn 68-80%)
- Lifting leg causes radicular pain of affected leg radiating to BELOW the knee
- Pain is worsened by ankle dorsiflexion
- Crossed Straight leg raise testing (high Sp, low Sn)
- Lifting the asymptomatic leg causes radicular pain down the affected leg
- Nerve root compromise
- Straight leg raise testing
- X-rays (if have red flag)
- Adults: AP + lateral of lumbar spine
- Children: add oblique views (to evaluate for spondylolisthesis)
- Labs
- CBC/ESR/Chem 7/UA (if >50 yo)
- MRI
- Indications:
- Suspect disk disease w/ severe motor impairment
- Suspect abscess or metastases w/ neuro involvement
- Indications:
- Cauda equina syndrome
- ?Elevated ESR
- US
- Rule-out AAA
See Also
Source
- Tintinalli