ACS - ECG: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(ST depression additions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==T Wave== | == T Wave == | ||
*Distribution | |||
**T wave is normally inverted in aVR; sometimes inverted in III, aVF, aVL, V1 | *Distribution | ||
*T-wave inversions in V2-V6 are always pathologic | **T wave is normally inverted in aVR; sometimes inverted in III, aVF, aVL, V1 | ||
*Morphology | *T-wave inversions in V2-V6 are always pathologic | ||
**Inverted, symmetric, | *Morphology | ||
**Transient changes suggests ischemia without infarction | **Inverted, symmetric, | ||
**Persistent changes suggests infarction (troponin elevation usually seen) | **Transient changes suggests ischemia without infarction | ||
*Pseudonormalization | **Persistent changes suggests infarction (troponin elevation usually seen) | ||
**In presence of baseline TWI (within 1 month), reocclusion causes normalization of TWI | *Pseudonormalization | ||
**In presence of baseline TWI (within 1 month), reocclusion causes normalization of TWI | |||
**Should be interpreted as evidence of ischemia | **Should be interpreted as evidence of ischemia | ||
==Q Wave== | == Q Wave == | ||
*Q waves do not always indicate infarction (see DDX below) | |||
*Must distinguish normal septal q waves from pathologic Q waves: | *Q waves do not always indicate infarction (see DDX below) | ||
**Normal septal q wave: | *Must distinguish normal septal q waves from pathologic Q waves: | ||
**Abnormal septal q wave: | **Normal septal q wave: <0.04s, low amplitude | ||
*Q-wave equivalents in the precordial leads: | **Abnormal septal q wave: >0.04s in I OR in II, III, AND aVF OR V3, V4, V5, AND V6 | ||
**R-wave diminution or poor R-wave progression | *Q-wave equivalents in the precordial leads: | ||
**Reverse R-wave progression (R waves increase then decrease in amplitude) | **R-wave diminution or poor R-wave progression | ||
***Must distinguish from lead misplacement | **Reverse R-wave progression (R waves increase then decrease in amplitude) | ||
***Must distinguish from lead misplacement | |||
**Tall R waves in V1, V2 (representing "Q waves" from posterior infarction) | **Tall R waves in V1, V2 (representing "Q waves" from posterior infarction) | ||
===Q Wave (Pathologic) DDX=== | === Q Wave (Pathologic) DDX === | ||
*Ischemic Q waves | |||
*LBBB | *Ischemic Q waves | ||
*LVH | *LBBB | ||
*Chronic lung disease | *LVH | ||
*Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | *Chronic lung disease | ||
*Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | |||
*Dilated cardiomyopathy | *Dilated cardiomyopathy | ||
==ST Segment Depression== | == ST Segment Depression == | ||
*Assume posterior STEMI or reciprocal changes to STEMI until proven otherwise | |||
*Indicators of ischemia: | *DDx: Post. STEMI, Subendocardial Infarct, Ischemia, Reciporical Changes, Strain c LVH, Dig effect | ||
** | *Contour: Most-->Least concerning for ischemia: Planar/Flat (90%) --> Concave up (33%) --> Downsloping with Asymmetric inverted T-wave (not ischemic/strain pattern) | ||
**Transient depression | *Assume posterior STEMI or reciprocal changes to STEMI until proven otherwise | ||
**Morphology that is flat or downsloping | *Indicators of ischemia: | ||
**>0.5mm depression from baseline (especially >1mm) in two or more contiguous leads | |||
**Transient depression | |||
**Morphology that is flat or downsloping | |||
*Strain: <br> | |||
**tall R wave | |||
**only in lateral leads (not anterior) | |||
**"checkbox" or asymmetric TWI | |||
**down sloping pattern | |||
== ST Segment Elevation == | |||
*Stage 1 | |||
*Stage 1 | **Timing: 30min - hours | ||
**Timing: 30min - hours | **Finding: hyperacute T waves | ||
**Finding: hyperacute T waves | ***>6mm limb leads | ||
*** | ***>10mm precordial leads | ||
*** | **Duration: normalizes in days, weeks, or months | ||
**Duration: normalizes in days, weeks, or months | *Stage 2 | ||
*Stage 2 | **Timing: minutes - hours | ||
**Timing: minutes - hours | **Finding: ST segment elevation | ||
**Finding: ST segment elevation | ***≥0.1mV in two or more contiguous leads | ||
***≥0.1mV in two or more contiguous leads | |||
**Duration: ST segment resolution occurs over 72hrs; completely resolves w/in 2-3wks | **Duration: ST segment resolution occurs over 72hrs; completely resolves w/in 2-3wks | ||
*Stage 3 | *Stage 3 | ||
**Timing: within 1hr; completed within 8-12hr | **Timing: within 1hr; completed within 8-12hr | ||
**Finding: Q waves | **Finding: Q waves | ||
**Duration: persist indefinitely in 70% of cases | **Duration: persist indefinitely in 70% of cases | ||
[[ | |||
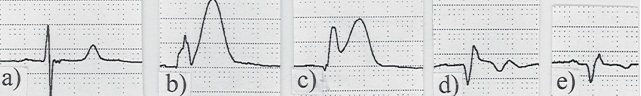
*a: 30min after chest pain onset | [[Image:STEMI Progression.jpg]] | ||
*b: 45min after chest pain onset (hyperacute T waves) | |||
*c: 70min after chest pain onset (ST elevation) | *a: 30min after chest pain onset | ||
*d: 3hr after PCI (ST segment has decreased, TWI incdicates reperfusion) | *b: 45min after chest pain onset (hyperacute T waves) | ||
*c: 70min after chest pain onset (ST elevation) | |||
*d: 3hr after PCI (ST segment has decreased, TWI incdicates reperfusion) | |||
*e: 5 days after PCI (ST segment back to baseline, TWI is near baseline) | *e: 5 days after PCI (ST segment back to baseline, TWI is near baseline) | ||
==Reciprocal Changes== | == Reciprocal Changes == | ||
#Anterior STEMI | |||
##Reciprocal ST-segment depression in at least one of leads II, III, aVF | #Anterior STEMI | ||
##Occurs in 40-70% of cases | ##Reciprocal ST-segment depression in at least one of leads II, III, aVF | ||
#Inferior STEMI | ##Occurs in 40-70% of cases | ||
##Reciprocal ST-segment depression usually present in I, aVL; often in V1-V3 | #Inferior STEMI | ||
##Occurs in 56% of cases | ##Reciprocal ST-segment depression usually present in I, aVL; often in V1-V3 | ||
#Posterior STEMI | ##Occurs in 56% of cases | ||
##Reciprocal ST-segment depression in V1-V4 | #Posterior STEMI | ||
###Differentiate from inf STEMI reciprocal depression based on upright T waves, posterior leads showing STEMI | ##Reciprocal ST-segment depression in V1-V4 | ||
###Differentiate from inf STEMI reciprocal depression based on upright T waves, posterior leads showing STEMI | |||
##Often associated w/ ST-segment elevation in II, III, aVF (inferior involvement) | ##Often associated w/ ST-segment elevation in II, III, aVF (inferior involvement) | ||
==See Also== | == See Also == | ||
*[[ACS - Anatomical Correlation]] | *[[ACS - Anatomical Correlation]] | ||
==Source== | == Source == | ||
*Electrocardiography in Emergency Medicine. ACEP Textbook. | *Electrocardiography in Emergency Medicine. ACEP Textbook. | ||
[[Category:Cards]] | [[Category:Cards]] | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 6 August 2012
T Wave
- Distribution
- T wave is normally inverted in aVR; sometimes inverted in III, aVF, aVL, V1
- T-wave inversions in V2-V6 are always pathologic
- Morphology
- Inverted, symmetric,
- Transient changes suggests ischemia without infarction
- Persistent changes suggests infarction (troponin elevation usually seen)
- Pseudonormalization
- In presence of baseline TWI (within 1 month), reocclusion causes normalization of TWI
- Should be interpreted as evidence of ischemia
Q Wave
- Q waves do not always indicate infarction (see DDX below)
- Must distinguish normal septal q waves from pathologic Q waves:
- Normal septal q wave: <0.04s, low amplitude
- Abnormal septal q wave: >0.04s in I OR in II, III, AND aVF OR V3, V4, V5, AND V6
- Q-wave equivalents in the precordial leads:
- R-wave diminution or poor R-wave progression
- Reverse R-wave progression (R waves increase then decrease in amplitude)
- Must distinguish from lead misplacement
- Tall R waves in V1, V2 (representing "Q waves" from posterior infarction)
Q Wave (Pathologic) DDX
- Ischemic Q waves
- LBBB
- LVH
- Chronic lung disease
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
ST Segment Depression
- DDx: Post. STEMI, Subendocardial Infarct, Ischemia, Reciporical Changes, Strain c LVH, Dig effect
- Contour: Most-->Least concerning for ischemia: Planar/Flat (90%) --> Concave up (33%) --> Downsloping with Asymmetric inverted T-wave (not ischemic/strain pattern)
- Assume posterior STEMI or reciprocal changes to STEMI until proven otherwise
- Indicators of ischemia:
- >0.5mm depression from baseline (especially >1mm) in two or more contiguous leads
- Transient depression
- Morphology that is flat or downsloping
- Strain:
- tall R wave
- only in lateral leads (not anterior)
- "checkbox" or asymmetric TWI
- down sloping pattern
ST Segment Elevation
- Stage 1
- Timing: 30min - hours
- Finding: hyperacute T waves
- >6mm limb leads
- >10mm precordial leads
- Duration: normalizes in days, weeks, or months
- Stage 2
- Timing: minutes - hours
- Finding: ST segment elevation
- ≥0.1mV in two or more contiguous leads
- Duration: ST segment resolution occurs over 72hrs; completely resolves w/in 2-3wks
- Stage 3
- Timing: within 1hr; completed within 8-12hr
- Finding: Q waves
- Duration: persist indefinitely in 70% of cases
- a: 30min after chest pain onset
- b: 45min after chest pain onset (hyperacute T waves)
- c: 70min after chest pain onset (ST elevation)
- d: 3hr after PCI (ST segment has decreased, TWI incdicates reperfusion)
- e: 5 days after PCI (ST segment back to baseline, TWI is near baseline)
Reciprocal Changes
- Anterior STEMI
- Reciprocal ST-segment depression in at least one of leads II, III, aVF
- Occurs in 40-70% of cases
- Inferior STEMI
- Reciprocal ST-segment depression usually present in I, aVL; often in V1-V3
- Occurs in 56% of cases
- Posterior STEMI
- Reciprocal ST-segment depression in V1-V4
- Differentiate from inf STEMI reciprocal depression based on upright T waves, posterior leads showing STEMI
- Often associated w/ ST-segment elevation in II, III, aVF (inferior involvement)
- Reciprocal ST-segment depression in V1-V4
See Also
Source
- Electrocardiography in Emergency Medicine. ACEP Textbook.