Digoxin toxicity: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
=== Risk Factors === | === Risk Factors === | ||
*Electrolyte Imbalance | |||
**[[Hypokalemia|Hyperkalemia]], [[Hypomagnesemia]], [[Hypercalcemia]] | |||
*Hypovolemia | |||
*Renal insufficiency | |||
*[[Cardiac Ischemia]] | |||
*[[Hypothyroidism]] | |||
*Meds | |||
**CCBs, amiodarone | |||
== Clinical Manifestations == | == Clinical Manifestations == | ||
===Cardiac=== | ===Cardiac=== | ||
*[[Syncope]] | |||
*Dysrhythmias | |||
**PVCs | |||
**[[Bradycardia]] | |||
**SVT w/ AV block | |||
**Junctional escape | |||
**Ventricular dysrhythmia, including bidirectional V-tach (esp in chronic toxicity) | |||
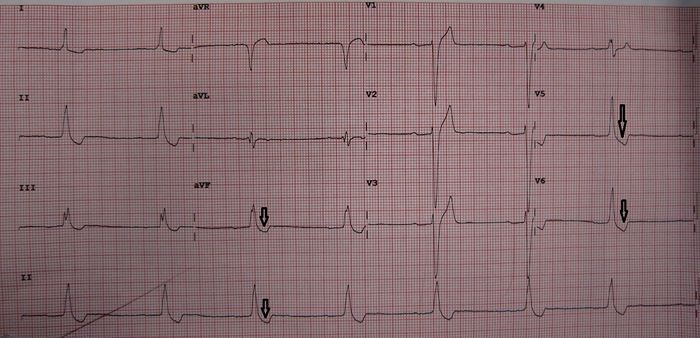
*Digitalis Effect (seen with therapeutic levels; not indicative of toxicity) | |||
**T wave changes (flattening or inversion) | |||
**QT interval shortening | |||
**Scooped ST segments with depression in lateral leads | |||
**Increased U-wave amplitude | |||
[[File:Digtox.jpg|center|700px]] | [[File:Digtox.jpg|center|700px]] | ||
===GI=== | ===GI=== | ||
*Often the earliest manifestation of toxicity | |||
**[[Nausea/vomiting]] | |||
**[[Abdominal Pain]] | |||
===Neuro=== | ===Neuro=== | ||
*[[Confusion]] | |||
*[[Weakness]] | |||
*Visual disturbances | |||
**Yellow halos | |||
**Scotomas | |||
*Delirium | |||
===Acute vs. Chronic=== | ===Acute vs. Chronic=== | ||
*Acute | |||
**Lower mortality | |||
**Bradycardia / AV block more common | |||
**Younger patients | |||
**Often don't need Fab | |||
*Chronic | |||
**Higher mortality | |||
**Ventricular dysrhythmias more common | |||
**Older patients | |||
**Often need Fab therapy | |||
==Work-Up== | ==Work-Up== | ||
*Dig level | |||
**Only useful prior to administration of [[Fab]] (otherwise becomes falsely elevated) | |||
*Chemistry | |||
*Urine output | |||
*ECG (serial) | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
*Must use H&P and labs in combination; no single element excludes or confirms the dx | |||
*Digoxin level | |||
**Normal = 0.5-2 ng/mL (ideal = 0.7-1.1) | |||
***May have toxicity even with "therapeutic" levels (esp w/ chronic toxicity) | |||
**Measure at least 6hr after acute ingestion (if stable); immediately for chronic ingestion | |||
***If measure before this may be falsely elevated due to incomplete drug distribution | |||
*Potassium level | |||
**Acute toxicity: Degree of [[Hyperkalemia]] correlates w/ degree of toxicity | |||
**Chronic toxicity: K+ may be normal/low (concomitant diuretic use) or high (renal failure) | |||
==DDX== | ==DDX== | ||
*CCB/BB toxicity | |||
*Clonidine toxicity | |||
*[[Organophosphate Toxicity]] | |||
*Sick sinus syndrome | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
'''Calcium is theoretically contradindicated in Dig Toxicity (see [[Stone Heart]])''' | '''Calcium is theoretically contradindicated in Dig Toxicity (see [[Stone Heart]])''' | ||
*'''[[Digoxin Immune Fab]]''' | |||
**Indications | |||
*** Ventricular dysrhythmias | |||
*** Symptomatic bradycardias unresponsive to atropine | |||
*** Hyerkalemia >5.0 mEq/L secondary to digitalis intoxicaiton | |||
*** Coningestions of cardiotoxic drugs (beta-blockers, cyclic antidepressants) | |||
*** Acute digoxin ingestion of greater than 10mg in adults or greater than 4mg in children | |||
*** Acute digoxin ingestions with post distribution digoxin >10ng/mL (by 6 hours post ingestion) | |||
*** Chronic digoxin ingestion leading to steady state serum digoxin concentrations of >4ng/ml | |||
*[[Activated Charcoal]] | |||
**Questionable efficacy | |||
**Only an adjunctive tx; NOT an alternative to fab fragment therapy | |||
**Consider only if present within 1 hr of ingestion | |||
**1g/kg (max 50g) | |||
===Dysrhythmias=== | ===Dysrhythmias=== | ||
*[[Digoxin Immune Fab]] is the agent of choice for all dysrhythmias! | |||
*[[Cardioversion]] should only be used as a last resort (may precipitate V-Fib) | |||
**Consider lower energy settings (25-50J) | |||
*Bradyarrhythmias (symptomatic) | |||
**[[Atropine]] 0.5mg IV | |||
**[[Pacing]] | |||
*Ventricular dysrhythmias | |||
**[[Dilantin Load|Phenytoin]] | |||
***Enhances AV conduction | |||
***Phenytoin: 15-20mg/kg at 50mg/min | |||
***Fosphenytoin: 15-20mg PE/kg at 100-150mg/min | |||
**[[Lidocaine]] | |||
***Decreases ventricular automaticity | |||
***1-3mg/kg over several minutes; follow by 1-4mg/min | |||
**[[Magnesium]] | |||
***Many patients have [[Hypomagnesemia]] and labs can be unreliable. | |||
***2-4 g IV over 20-60 mins | |||
===[[Hyperkalemia]]=== | ===[[Hyperkalemia]]=== | ||
*Treat with [[Fab]], not with usual meds | |||
**Once Fab is given hyperkalemia will rapidly correct | |||
*If [[Fab]] unavailable and hyperkalemia is life-threatening then treat with: | |||
**Glucose-insulin | |||
**Sodium bicarb | |||
**Kayexelate | |||
**Dialysis | |||
**Calcium (controversial: some say dangerous, others say not) | |||
===[[Hypokalemia]]=== | ===[[Hypokalemia]]=== | ||
*Chronic intoxication | |||
**Raise level to 3.5-4 | |||
*Acute intoxication | |||
**Do not treat (likely that potassium level is rapidly rising) | |||
===[[Hypomagnesemia]]=== | ===[[Hypomagnesemia]]=== | ||
*Treat with 1-2g over 10-20 min | |||
**Monitor for resp depresion | |||
**Avoid in pts with: | |||
***Renal failure | |||
***Bradydysrhythmias/conduction blocks | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
*[[Digoxin]] | *[[Digoxin]] | ||
== | == References == | ||
[[Category:Cards]] | [[Category:Cards]] | ||
[[Category:Drugs]] | [[Category:Drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Tox]] | [[Category:Tox]] | ||
Revision as of 12:09, 3 September 2015
Background
- Mechanism of action
- Positive inotropic effect
- Inhibits Na-K pump -> incr extracelluar K, incr intracellular Na -> incr intracellular Ca
- Increases vagal tone
- Can lead to bradyarrhythmias (esp in young)
- Increases automaticity
- Can lead to tachyarrhythmias (esp in elderly)
- Positive inotropic effect
- Renally cleared
- Hemodialysis does not work
- Can also be found in nature: Foxglove, Oleander, certain toads
Risk Factors
- Electrolyte Imbalance
- Hypovolemia
- Renal insufficiency
- Cardiac Ischemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Meds
- CCBs, amiodarone
Clinical Manifestations
Cardiac
- Syncope
- Dysrhythmias
- PVCs
- Bradycardia
- SVT w/ AV block
- Junctional escape
- Ventricular dysrhythmia, including bidirectional V-tach (esp in chronic toxicity)
- Digitalis Effect (seen with therapeutic levels; not indicative of toxicity)
- T wave changes (flattening or inversion)
- QT interval shortening
- Scooped ST segments with depression in lateral leads
- Increased U-wave amplitude
GI
- Often the earliest manifestation of toxicity
Neuro
Acute vs. Chronic
- Acute
- Lower mortality
- Bradycardia / AV block more common
- Younger patients
- Often don't need Fab
- Chronic
- Higher mortality
- Ventricular dysrhythmias more common
- Older patients
- Often need Fab therapy
Work-Up
- Dig level
- Only useful prior to administration of Fab (otherwise becomes falsely elevated)
- Chemistry
- Urine output
- ECG (serial)
Diagnosis
- Must use H&P and labs in combination; no single element excludes or confirms the dx
- Digoxin level
- Normal = 0.5-2 ng/mL (ideal = 0.7-1.1)
- May have toxicity even with "therapeutic" levels (esp w/ chronic toxicity)
- Measure at least 6hr after acute ingestion (if stable); immediately for chronic ingestion
- If measure before this may be falsely elevated due to incomplete drug distribution
- Normal = 0.5-2 ng/mL (ideal = 0.7-1.1)
- Potassium level
- Acute toxicity: Degree of Hyperkalemia correlates w/ degree of toxicity
- Chronic toxicity: K+ may be normal/low (concomitant diuretic use) or high (renal failure)
DDX
- CCB/BB toxicity
- Clonidine toxicity
- Organophosphate Toxicity
- Sick sinus syndrome
Treatment
Calcium is theoretically contradindicated in Dig Toxicity (see Stone Heart)
- Digoxin Immune Fab
- Indications
- Ventricular dysrhythmias
- Symptomatic bradycardias unresponsive to atropine
- Hyerkalemia >5.0 mEq/L secondary to digitalis intoxicaiton
- Coningestions of cardiotoxic drugs (beta-blockers, cyclic antidepressants)
- Acute digoxin ingestion of greater than 10mg in adults or greater than 4mg in children
- Acute digoxin ingestions with post distribution digoxin >10ng/mL (by 6 hours post ingestion)
- Chronic digoxin ingestion leading to steady state serum digoxin concentrations of >4ng/ml
- Indications
- Activated Charcoal
- Questionable efficacy
- Only an adjunctive tx; NOT an alternative to fab fragment therapy
- Consider only if present within 1 hr of ingestion
- 1g/kg (max 50g)
Dysrhythmias
- Digoxin Immune Fab is the agent of choice for all dysrhythmias!
- Cardioversion should only be used as a last resort (may precipitate V-Fib)
- Consider lower energy settings (25-50J)
- Bradyarrhythmias (symptomatic)
- Ventricular dysrhythmias
- Phenytoin
- Enhances AV conduction
- Phenytoin: 15-20mg/kg at 50mg/min
- Fosphenytoin: 15-20mg PE/kg at 100-150mg/min
- Lidocaine
- Decreases ventricular automaticity
- 1-3mg/kg over several minutes; follow by 1-4mg/min
- Magnesium
- Many patients have Hypomagnesemia and labs can be unreliable.
- 2-4 g IV over 20-60 mins
- Phenytoin
Hyperkalemia
- Treat with Fab, not with usual meds
- Once Fab is given hyperkalemia will rapidly correct
- If Fab unavailable and hyperkalemia is life-threatening then treat with:
- Glucose-insulin
- Sodium bicarb
- Kayexelate
- Dialysis
- Calcium (controversial: some say dangerous, others say not)
Hypokalemia
- Chronic intoxication
- Raise level to 3.5-4
- Acute intoxication
- Do not treat (likely that potassium level is rapidly rising)
Hypomagnesemia
- Treat with 1-2g over 10-20 min
- Monitor for resp depresion
- Avoid in pts with:
- Renal failure
- Bradydysrhythmias/conduction blocks
External Links
Disposition
- Admit for signs of toxicity or history of large ingested dose; admit to ICU if Fab given
- Discharge after 12hr observation if asymptomatic after accidental overdose