Tibial plateau fracture: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[[File:Knee diagram2.png|thumb|Anatomy of anterolateral aspect of right knee.]] | |||
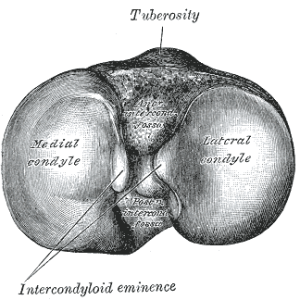
[[File:Gray257.png|thumb|Superior surface of right tibia. (Anterior is at top of image.)]] | |||
*ACL and MCL injuries associated with lateral plateau fracture | |||
*PCL and LCL associated with medial plateau fracture | |||
*[[Compartment syndrome]] may occur | |||
*[[Segond fracture]] | |||
**Avulsion fracture of margin of lateral tibial plateau just below joint line | |||
**Associated with tear of ACL and meniscal ligaments | |||
==Clinical Features== | |||
*Occurs via axial load that drives femoral condyle into tibia | *Occurs via axial load that drives femoral condyle into tibia | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
{{Knee DDX}} | |||
{{Distal leg fractures DDX}} | |||
==Evaluation== | |||
[[File:Schatzker Classification.jpg|thumb|Schatzker Classification of Tibial Plateau Fractures]] | |||
===Imaging=== | ===Imaging=== | ||
*AP, lateral, oblique views (internal for lateral plateau, external for medial plateau) | [[File:TibPlatFracPlainMark.png|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Lipohemarthrosis.png|thumb|Lipohemarthrosis (presence of fat and blood from bone marrow in the joint space after an intraarticular fracture) seen on X-ray in a person with a subtle tibial plateau fracture]] | |||
[[File:TibPlateauBadMark.png|thumb]] | |||
*AP, lateral, oblique views (internal for lateral plateau, external for medial plateau). Tunnel view may also be helpful. | |||
**AP - line drawn at lateral margin of femur should not have >5mm of tibia beyond it | **AP - line drawn at lateral margin of femur should not have >5mm of tibia beyond it | ||
*CT or MRI should be considered if plain film negative but high clinical suspicion | *CT or MRI should be considered if plain film negative but high clinical suspicion based on mechanism or inability to bear weight | ||
===Schatzker Classification=== | ===Schatzker Classification=== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 33: | ||
*Schatzker IV Pure medial depression | *Schatzker IV Pure medial depression | ||
*Schatzker V Bicondylar | *Schatzker V Bicondylar | ||
*Schatzker VI Split extends to metadiaphysis | *Schatzker VI Split extends to metadiaphysis | ||
==Management== | |||
{{General Fracture Management}} | |||
== | ===Specific Management=== | ||
*Knee immobilizer with non-weightbearing and ortho referral in 2-7d | |||
*Emergent surgical management if open or if neurovascular compromise | |||
==Disposition== | |||
*Outpatient follow up | |||
== | ===Indications for Expedited Referral (within 48hr)=== | ||
* | *Significant displacement or depression | ||
*Suspected or documented ligamentous injury | |||
== | ===Indications for (outpatient) surgery=== | ||
* | *Articular stepoff > 3mm | ||
** | *Condylar widening > 5mm | ||
** | *Varus/valgus instability | ||
*All medial plateau fractures | |||
*All bicondylar fractures | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 60: | ||
*[[Knee (Main)]] | *[[Knee (Main)]] | ||
== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | [[Category:Orthopedics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:03, 5 March 2025
Background
- ACL and MCL injuries associated with lateral plateau fracture
- PCL and LCL associated with medial plateau fracture
- Compartment syndrome may occur
- Segond fracture
- Avulsion fracture of margin of lateral tibial plateau just below joint line
- Associated with tear of ACL and meniscal ligaments
Clinical Features
- Occurs via axial load that drives femoral condyle into tibia
Differential Diagnosis
Knee diagnoses
Acute knee injury
- Knee dislocation
- Knee fractures
- Meniscus and ligament knee injuries
- Patella dislocation
- Patellar tendonitis
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
Nontraumatic/Subacute
- Arthritis
- Gout and Pseudogout
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
- Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner's Knee)
- Patellar tendonitis (Jumper's knee)
- Pes anserine bursitis
- Popliteal cyst (Bakers cyst)
- Prepatellar bursitis (nonseptic)
- Septic bursitis
- Septic joint
- DVT
Distal Leg Fracture Types
- Tibial plateau fracture
- Tibial shaft fracture
- Pilon fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- Tibia fracture (peds)
- Ankle fracture
- Foot and toe fractures
Evaluation
Imaging
- AP, lateral, oblique views (internal for lateral plateau, external for medial plateau). Tunnel view may also be helpful.
- AP - line drawn at lateral margin of femur should not have >5mm of tibia beyond it
- CT or MRI should be considered if plain film negative but high clinical suspicion based on mechanism or inability to bear weight
Schatzker Classification
- Schatzker I Lateral split
- Schatzker II Split with depression
- Schatzker III Pure lateral depression
- Schatzker IV Pure medial depression
- Schatzker V Bicondylar
- Schatzker VI Split extends to metadiaphysis
Management
General Fracture Management
- Acute pain management
- Open fractures require immediate IV antibiotics and urgent surgical washout
- Neurovascular compromise from fracture requires emergent reduction and/or orthopedic intervention
- Consider risk for compartment syndrome
Specific Management
- Knee immobilizer with non-weightbearing and ortho referral in 2-7d
- Emergent surgical management if open or if neurovascular compromise
Disposition
- Outpatient follow up
Indications for Expedited Referral (within 48hr)
- Significant displacement or depression
- Suspected or documented ligamentous injury
Indications for (outpatient) surgery
- Articular stepoff > 3mm
- Condylar widening > 5mm
- Varus/valgus instability
- All medial plateau fractures
- All bicondylar fractures