Anatomic planes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
*l: Left-right, or lateral axis (cyan, blue-green | *l: Left-right, or lateral axis (cyan, blue-green | ||
*m: Medial or anterior-posterior axis (magenta) | *m: Medial or anterior-posterior axis (magenta) | ||
The figure shows three major planes annotated as follows: | The figure shows three major planes annotated as follows: | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
*c: Coronal plane (green), containing the axial axis and the lateral axis | *c: Coronal plane (green), containing the axial axis and the lateral axis | ||
*s: Sagittal plane (red), containing the axial axis and the medial axis | *s: Sagittal plane (red), containing the axial axis and the medial axis | ||
There also is: | There also is: | ||
Latest revision as of 23:01, 22 October 2025
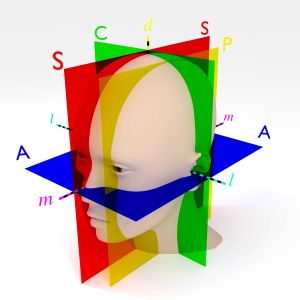
The figure shows three axes annotated as follows:
- d: Dorsoventral or Axial axis (yellow)
- l: Left-right, or lateral axis (cyan, blue-green
- m: Medial or anterior-posterior axis (magenta)
The figure shows three major planes annotated as follows:
- a: Axial or horizontal plane (blue), that contains the lateral axis and also the medial axis
- c: Coronal plane (green), containing the axial axis and the lateral axis
- s: Sagittal plane (red), containing the axial axis and the medial axis
There also is:
- e: The eye position showing the anterior end of the brain
- p: an example of a parasagittal plane (yellow); parasagittal planes comprise the class of planes parallel to (and therefore lateral to)