Lung abscess: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "==Background== *Localized, suppurative necrotizing process occurring w/in the pulmonary parenchyma ==Causes== *Aspiration PNA *Bacteremia from nonpulmonary infection *Pulmonary ...") |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
*Localized, suppurative necrotizing process occurring | [[File:Lung and diaphragm.jpg|thumb|Lobes of the lung with related anatomy.]] | ||
*Localized, suppurative necrotizing process occurring within the pulmonary parenchyma | |||
*Microbiology | |||
**Community-acquired: [[anaerobes]] mostly aspiration, anaerobic bacteria from oral cavity: peptostreptococcus, prevotella, bacteroides, fusobacterium species | |||
**Hospital-acquired: [[Staph]], [[E coli]], [[Klebsiella]], [[pseudomonas]], [[legionella]] | |||
==Causes== | ===Causes=== | ||
*Aspiration | *Aspiration [[pneumonia]] (7-14 days to become lung abscess) | ||
*Bacteremia from nonpulmonary infection | *[[Bacteremia]] from nonpulmonary infection | ||
*[[Influenza]] leading to Bacterial superinfection (e.g. ''S. Aureus'') | |||
*Pulmonary infarction | *Pulmonary infarction | ||
*Infection as a result of penetrating chest trauma | *Infection as a result of penetrating [[chest trauma]] | ||
*Primary and metastatic neoplasms | *Primary and metastatic neoplasms | ||
*Wegener's, sarcoidosis | *[[Granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Wegener's), [[sarcoidosis]] | ||
== | ==Clinical Features== | ||
*[[Cough]], [[fever]], pleuritic [[chest pain]], weight loss, night sweats (generally over course of several weeks) | |||
**[[Tachycardia]], [[tachypnea]], or [[fever]] may be absent | |||
===Complications=== | |||
*[[Empyema]] | |||
*Massive [[hemoptysis]] | |||
== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
*Cavitary lesion with air-fluid level | |||
*Infected bullae | |||
*Pleural fluid collection with bronchopleural fistula | |||
*Loop of bowel extending through diaphragmatic hernia | |||
==Evaluation== | |||
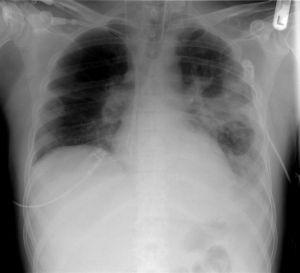
[[File:PulmonaryabsCXR.png|thumb|Pulmonary abscess on [[CXR]]]] | |||
[[File:XR chest - pneumonia with abscess and caverns - d0.jpg |thumb|[[CXR]] showing pneumonia with [[lung abscess]].]] | |||
[[File:Pulmonaryabs.png|thumb|Pulmonary abscess on CT scan]] | |||
*[[CXR]] or CT Chest | |||
*Dense consolidation with air-fluid level inside of a thick-walled cavitary lesion | |||
**Air-fluid level indicates communication of [[abscess]] cavity with a bronchiole | |||
== | ==Management== | ||
*Medical management will successfully treat 70-90% of lung abscesses | |||
**Drainage occurs spontaneously from communication of cavity with tracheobronchial tree | |||
**Bronchoscopic drainage may result in seeding other parts of the lung | |||
*Antibiotics | |||
**[[Clindamycin]] + 2nd or 3rd gen [[cephalosporin]] '''OR''' | |||
**[[Clindamycin]] + [[ampicillin/sulbactam]] | |||
==Disposition== | ==Disposition== | ||
*Admit | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Empyema]] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
<References/> | |||
[[Category:ID]] | [[Category:ID]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Pulmonary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:16, 13 December 2023
Background
- Localized, suppurative necrotizing process occurring within the pulmonary parenchyma
- Microbiology
- Community-acquired: anaerobes mostly aspiration, anaerobic bacteria from oral cavity: peptostreptococcus, prevotella, bacteroides, fusobacterium species
- Hospital-acquired: Staph, E coli, Klebsiella, pseudomonas, legionella
Causes
- Aspiration pneumonia (7-14 days to become lung abscess)
- Bacteremia from nonpulmonary infection
- Influenza leading to Bacterial superinfection (e.g. S. Aureus)
- Pulmonary infarction
- Infection as a result of penetrating chest trauma
- Primary and metastatic neoplasms
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's), sarcoidosis
Clinical Features
- Cough, fever, pleuritic chest pain, weight loss, night sweats (generally over course of several weeks)
- Tachycardia, tachypnea, or fever may be absent
Complications
- Empyema
- Massive hemoptysis
Differential Diagnosis
- Cavitary lesion with air-fluid level
- Infected bullae
- Pleural fluid collection with bronchopleural fistula
- Loop of bowel extending through diaphragmatic hernia
Evaluation

Pulmonary abscess on CXR
- CXR or CT Chest
- Dense consolidation with air-fluid level inside of a thick-walled cavitary lesion
- Air-fluid level indicates communication of abscess cavity with a bronchiole
Management
- Medical management will successfully treat 70-90% of lung abscesses
- Drainage occurs spontaneously from communication of cavity with tracheobronchial tree
- Bronchoscopic drainage may result in seeding other parts of the lung
- Antibiotics
- Clindamycin + 2nd or 3rd gen cephalosporin OR
- Clindamycin + ampicillin/sulbactam
Disposition
- Admit