Impetigo: Difference between revisions
Mceledon83 (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
**Mupirocin ointment 2% TID x 7-14d | **Mupirocin ointment 2% TID x 7-14d | ||
*Oral abx | *Oral abx | ||
**Consider for large areas or if topical tx is impractical or for bullous impetigo | **Consider for large areas or if topical tx is impractical or for [[bullous impetigo]] | ||
**Clindamycin 24mg/kg/d in 3 doses x7-10d | **[[Clindamycin]] 24mg/kg/d in 3 doses x7-10d | ||
==Source== | ==Source== | ||
Revision as of 06:14, 8 March 2014
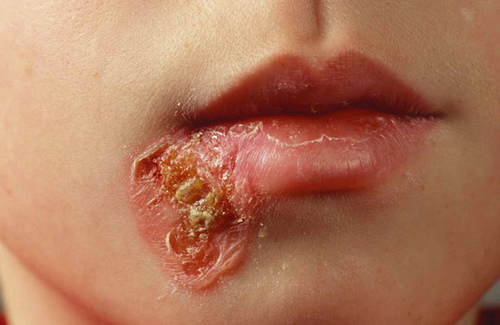
Background
- Superficial epidermal infection characterized by amber crusts (nonbullous) or vesicles (bullous)
- May be super-infection or primary infection
- Fever and systemic signs are uncommon
Diagnosis
- Nonbullous
- Erythematous macules/papules develop into vesicles which become pustular and rupture
- As rupture release yellow fluid which dries to form stratified golden crust
- Erythematous macules/papules develop into vesicles which become pustular and rupture
- Bullous
- Bullae form as result of staph toxin
- Some cases caused by MRSA
Treatment
- Topical abx
- Mupirocin ointment 2% TID x 7-14d
- Oral abx
- Consider for large areas or if topical tx is impractical or for bullous impetigo
- Clindamycin 24mg/kg/d in 3 doses x7-10d
Source
Tintinalli